Office 365 Configuration
Overview
Integration of Microsoft Office 365 with the Binadox SaaS and IaaS usage monitoring and cost optimization platform allows you to get Office 365 spend and utilization insights and usage analysis of Office 365 features on a per-user basis, as well as to receive cost optimization recommendations. Additionally, if you have a single sign-on (SSO) method enabled, Binadox will discover applications used by employees in your enterprise that are authenticated to via SSO. The system will notify you of discovered applications available for integration with Binadox to receive their usage and spend data.
For Application Discovery with Office 365, you require Azure Active Directory Premium P1 or P2 licenses.
This guide provides step-by-step instructions on how to integrate Microsoft Office 365 with Binadox. To successfully connect Binadox with your Office 365 account, the following parameters are required: a Tenant domain, an Application ID and a Client Secret of an application registered with Azure Active Directory, and login credentials. For safety reasons, create a new user and assign him a restricted role with limited access to your Microsoft tenant. There are two options to generate the required parameters:
Option 1. Use Windows PowerShell. Download and unzip the script file. Run it using the PowerShell commands. PowerShell will automatically generate all the required parameters (see Clause 1 for step-by-step instructions).
Option 2. On the Microsoft Azure portal, register the Binadox application. In the Microsoft 365 admin center, create a new user to represent Binadox and assign him a restricted role with limited access to your Microsoft tenant (see Clause 2 for step-by-step instructions).
Cost optimization and usage monitoring are available only for paid Office 365 subscriptions.
Option 1. PowerShell
1.1 Change a PowerShell Execution Policy
1. Download the file. Extract the .ps1 file from the zipped file.
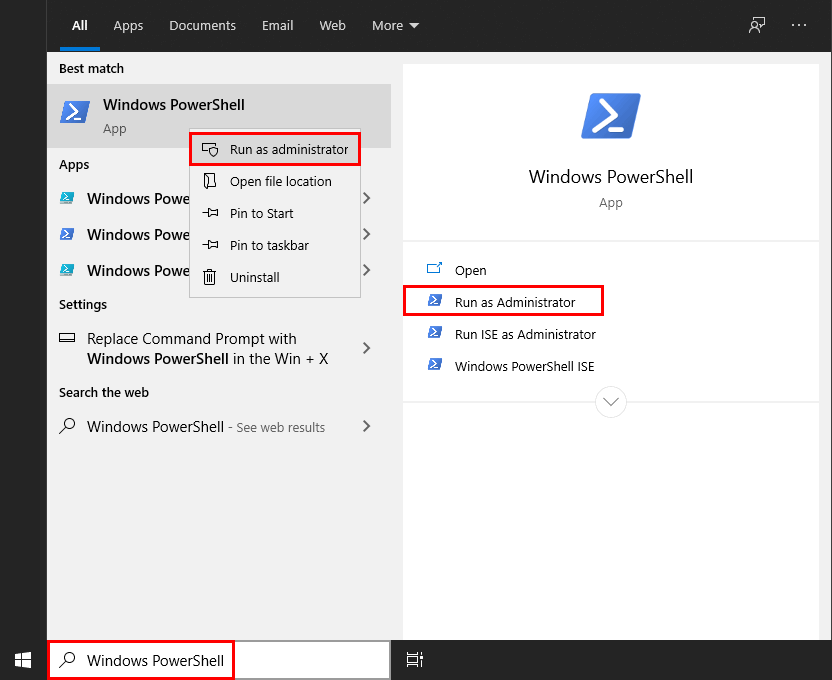
2. On your Windows computer, type “PowerShell” in the search box next to the Start Menu. Right-click the app name and select the Run as Administrator option in the drop-down list.
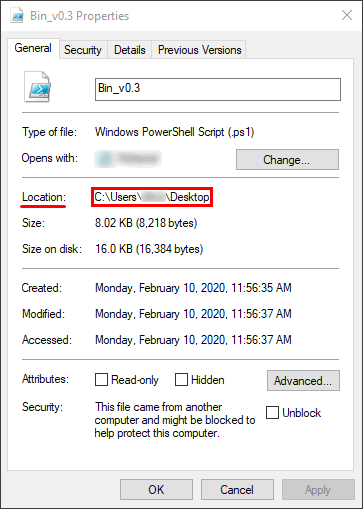
3. Right-click the downloaded .ps1 file and select Properties in the drop-down list. On the General tab, copy the file location.
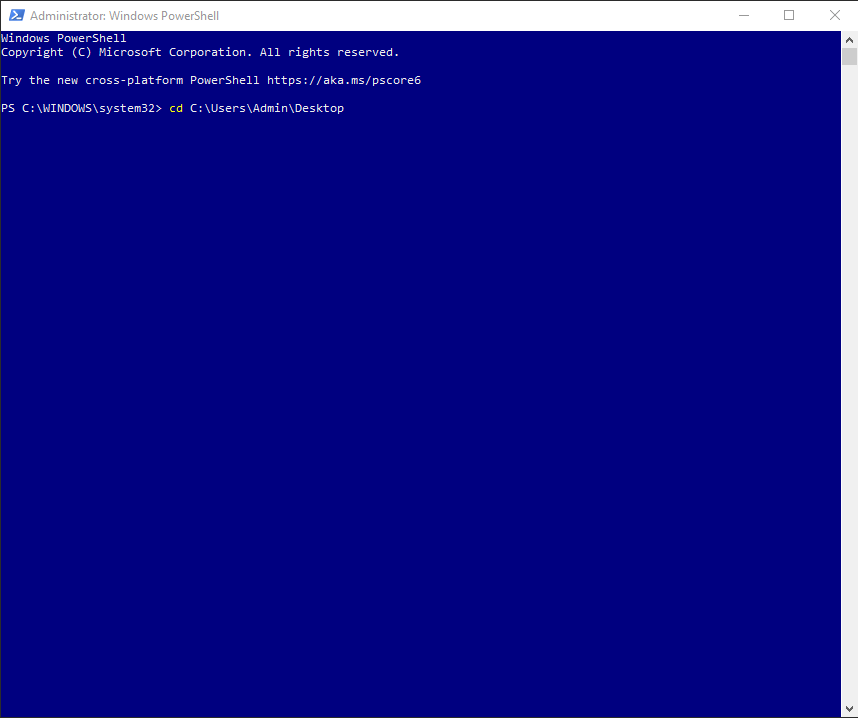
4. Change the default directory to the one of the downloaded .ps1 file by entering the cd command and specifying the file location, e.g. cd C:Users/Admin/Desktop. Press Enter.
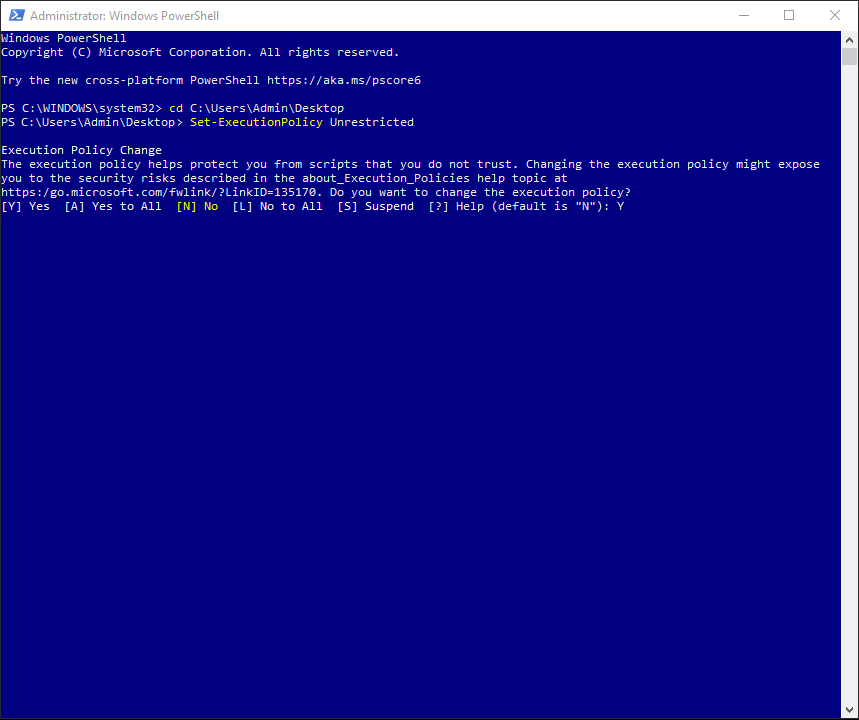
5. The default execution policy for Windows client computers is Restricted. To see the effective execution policy for the current session, use the Get-ExecutionPolicy cmdlet. To allow running unsigned script files, change the Restricted execution policy into Unrestricted. Use the Set-ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted cmdlet. Choose the Yes option by typing Y. Press Enter.
1.2 Run the Script
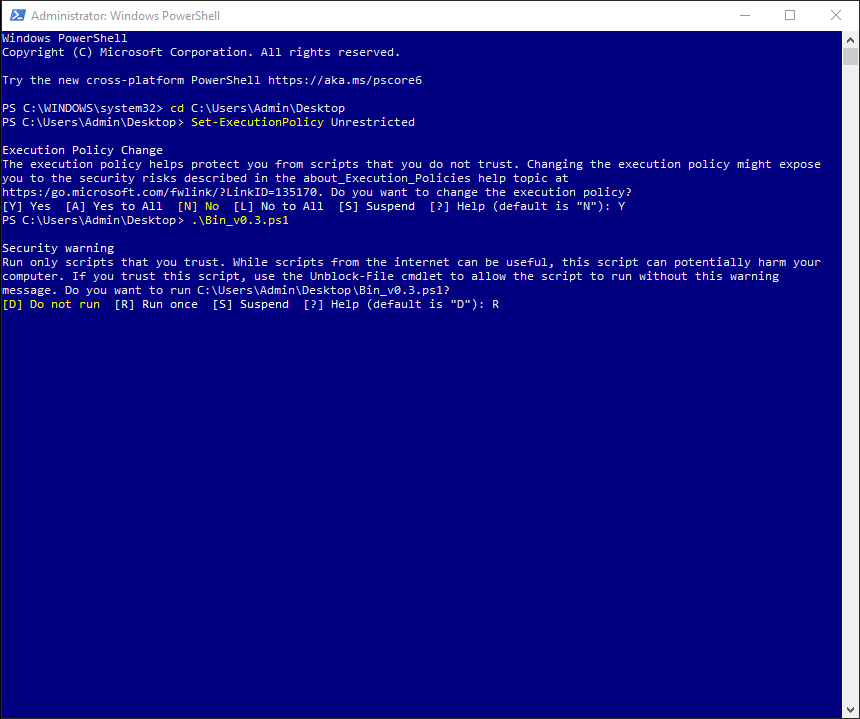
Make sure to extract the .ps1 file from the zipped file. Type ./Bin_v0.3.ps1 (the name of the downloaded file with the ./ prefix, with or without the .ps1 extension). Press Enter.
To allow PowerShell to run the script, choose the Run once option by typing R. Press Enter.
1.3 Install the NuGet Provider
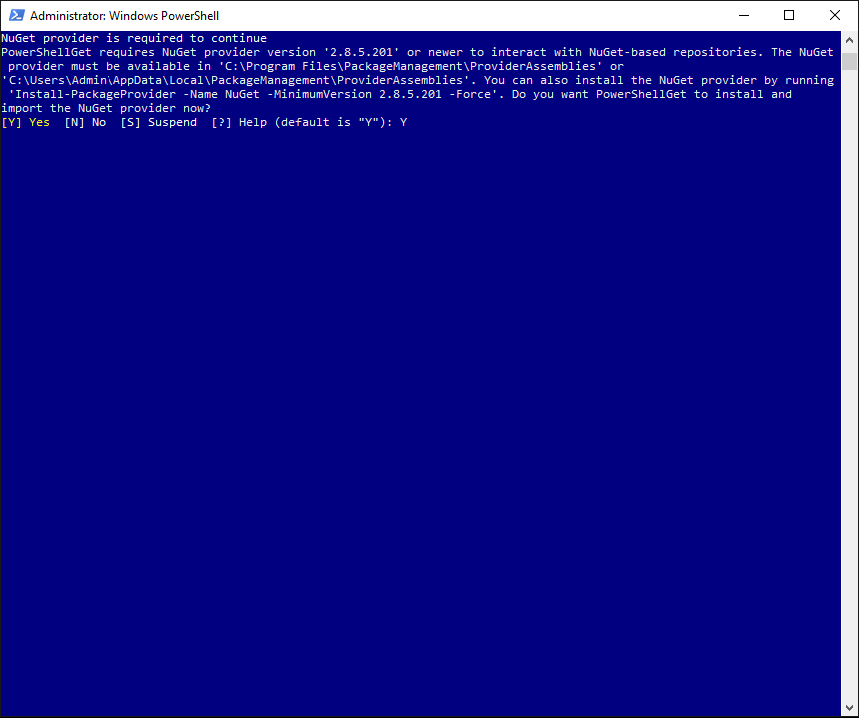
In case the NuGet Provider has not been installed on your Windows computer, the prompt message will require you to do so. To allow the PowerShellGet module to install and import the NuGet provider, choose the Yes option by typing Y. Press Enter.
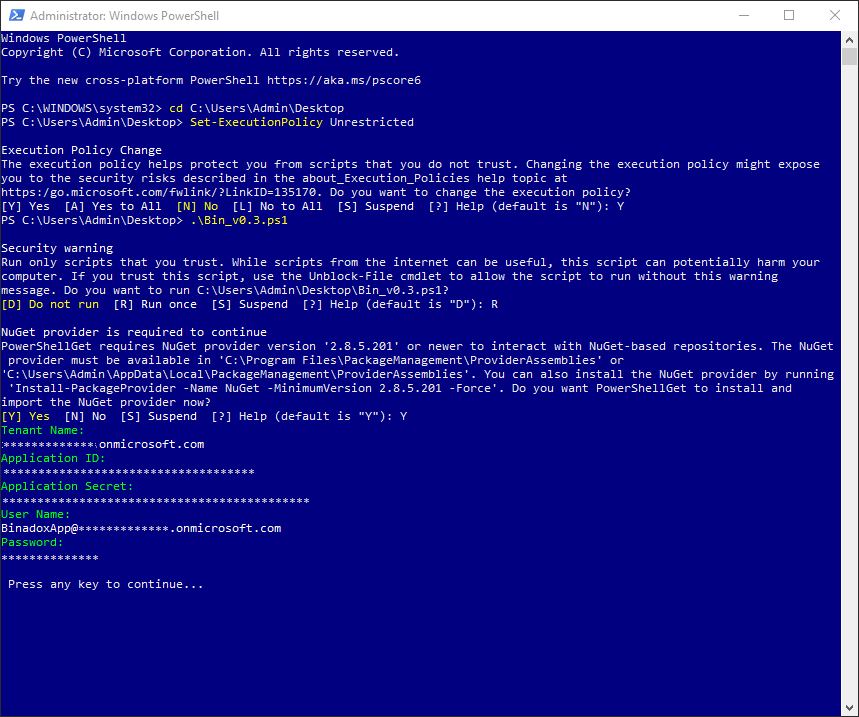
1.4 Copy Generated Parameters
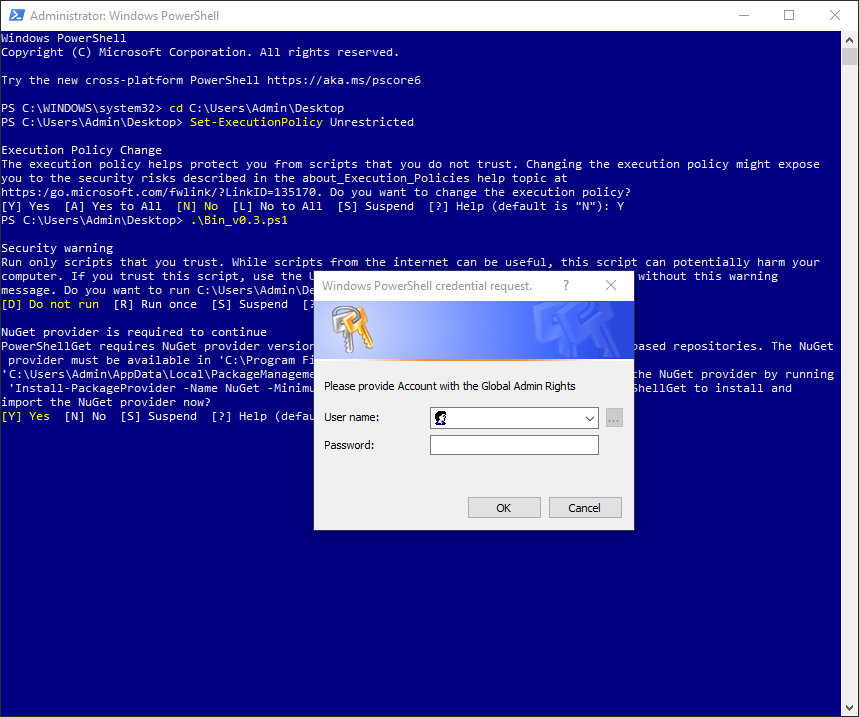
1. Global administrator permissions are required to continue. In the appeared PowerShell credential request window, type in Office 365 global administrator credentials. Click Ok.
2. Copy generated configuration parameters: Tenant domain, Application ID, Client Secret and credentials of a new user with limited access to your Microsoft tenant.
1.5 Return the Default Execution Policy
Press any key to continue. To return the default Restricted execution policy, use the Set-ExecutionPolicy Restricted cmdlet. Choose the Yes option by typing Y. Press Enter.
See Clause 3 on how to connect Office 365 with Binadox.
Option 2. Azure AD and Microsoft 365 Admin Center
2.1 Register Binadox with Azure AD
To register Binadox with Azure Active Directory, you need a subscription to Office 365 and a subscription to Azure associated with the Office 365 subscription.
1. Sign in to the Microsoft Azure portal as a global administrator using credentials of your Microsoft tenant that has the subscription to Office 365 you wish to use for Binadox spend and usage optimization.
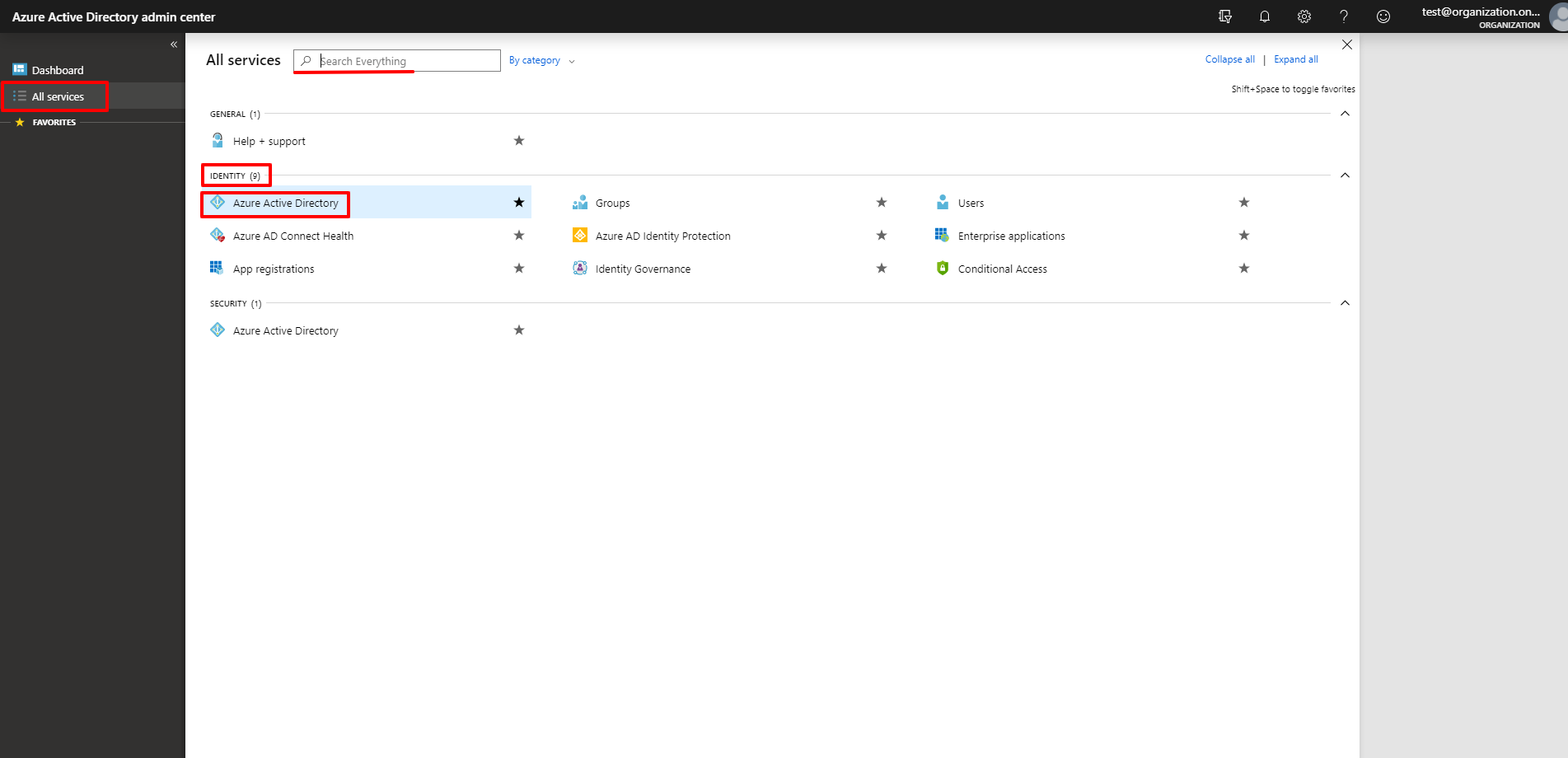
2. In the navigation pane on the left, click All services > Identity > Azure Active Directory. Use the search bar, if necessary.
Advice: For your convenience, click on the star icon near the Azure Active Directory service name to add it to the Favorites category in the navigation pane.
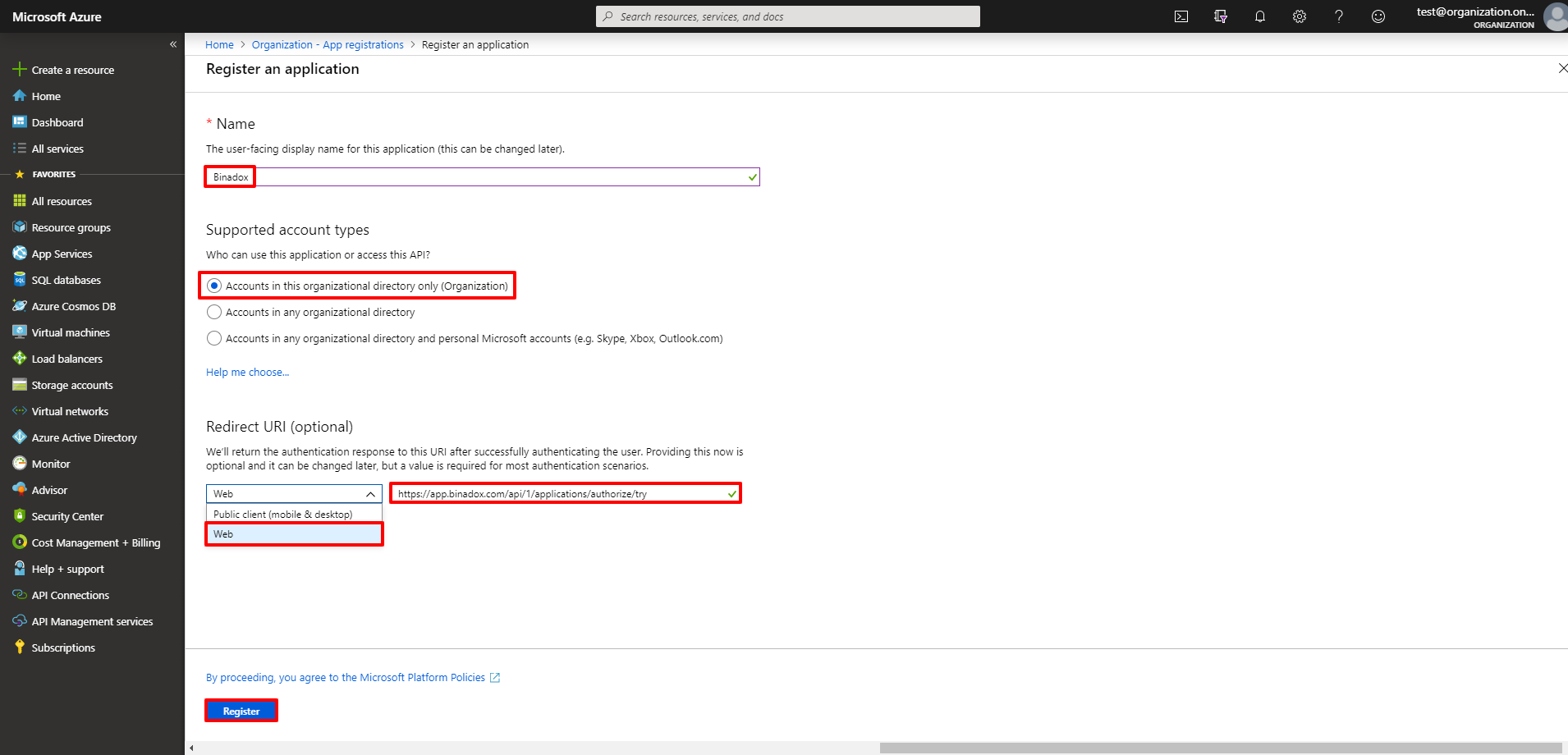
3. Go to the App registrations section and click the New registration button.
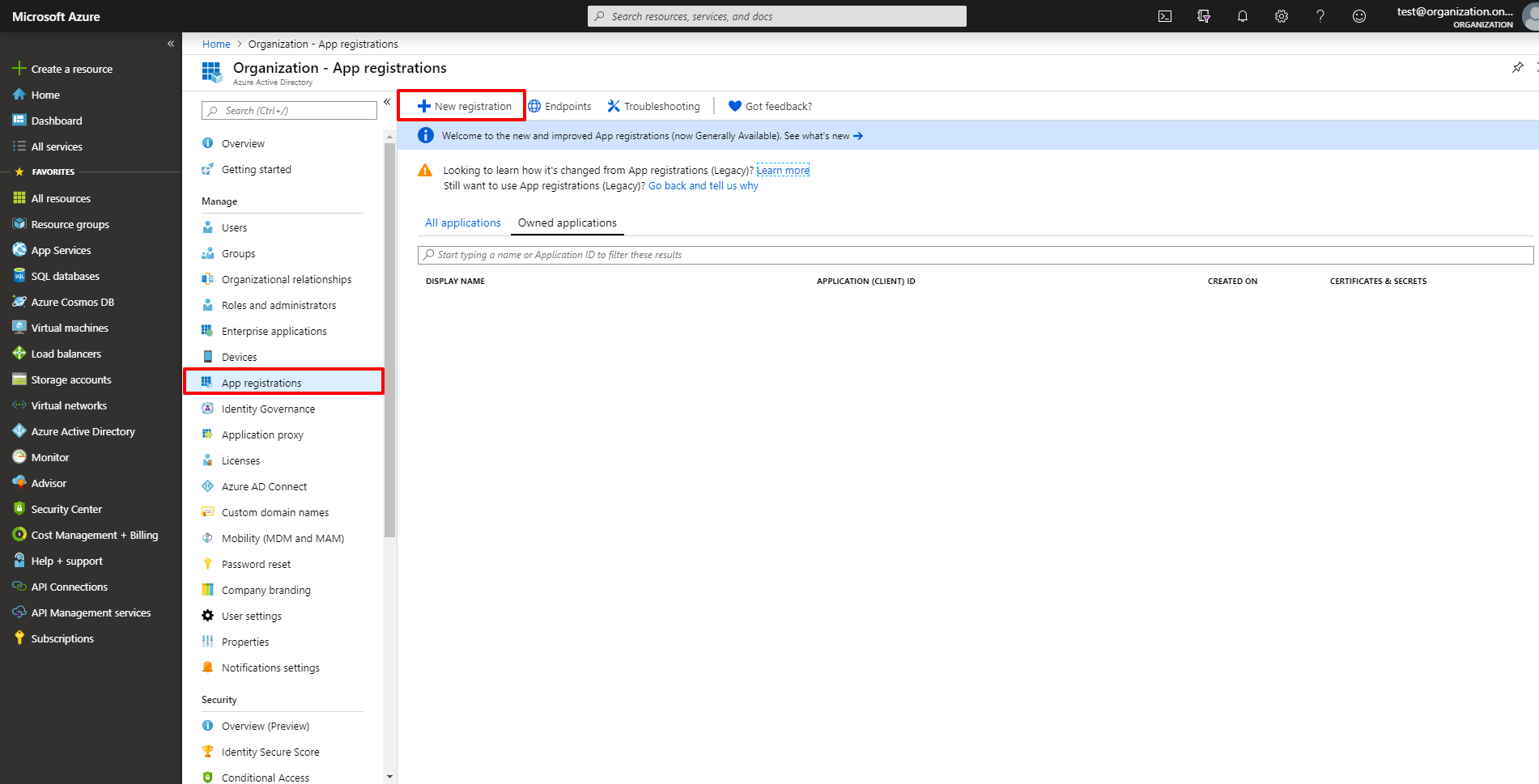
4. Fill in the following fields in the registration form:
• Enter an application name in the Name field (e.g. Binadox).
• Check the Accounts in the organizational directory only checkbox in the Supported account types field.
• In the Redirect URI (optional) section, select Web in the drop-down list. Enter the following URL:
https://app.binadox.com/api/1/applications/authorize/try
Click the Register button to complete the registration.
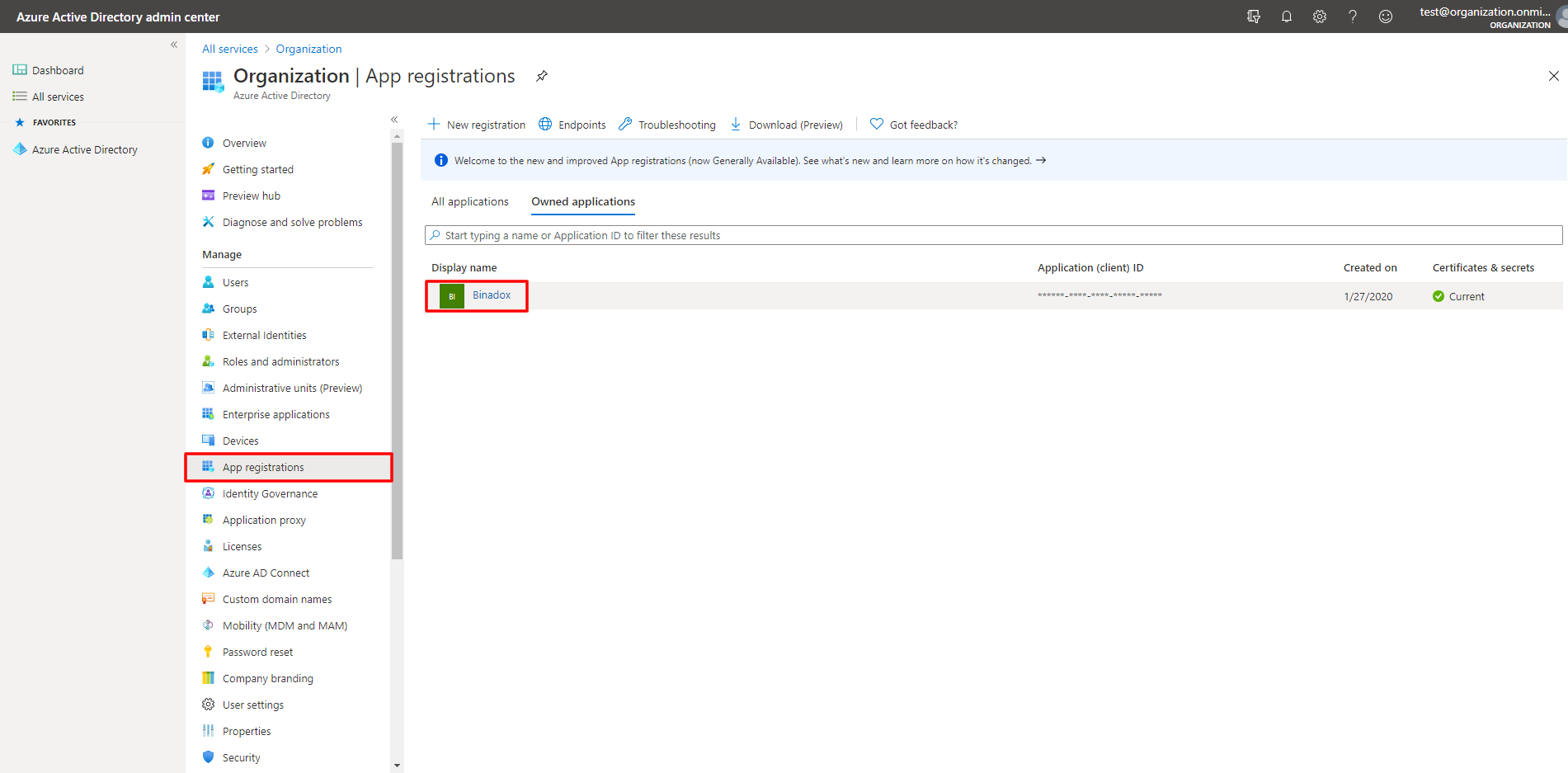
5. On the App registrations page, click on the name of a newly registered application.
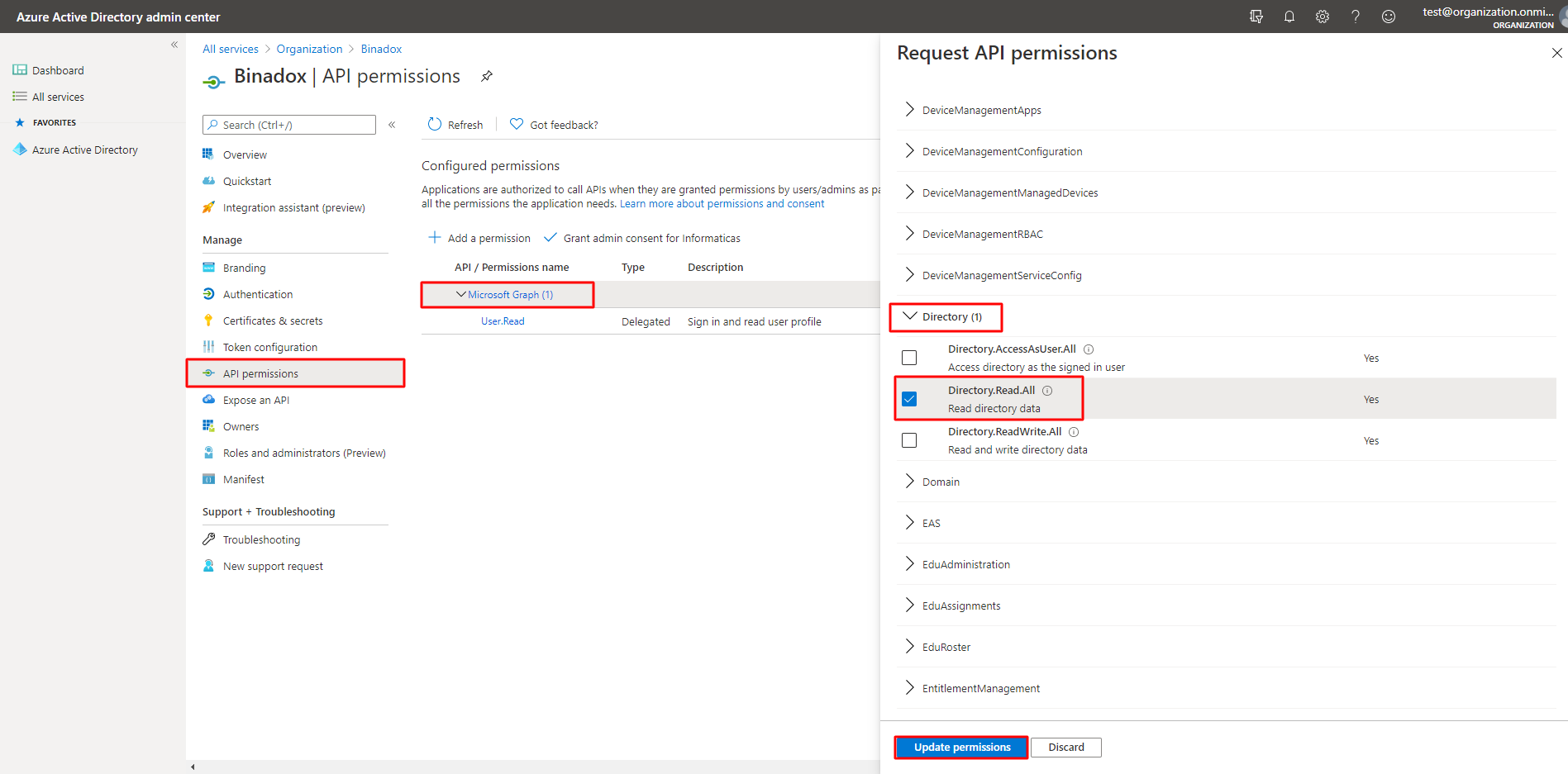
6. In the navigation pane, choose API permissions. Under API/Permissions name, click Microsoft Graph. On the Request API permissions page that opens, choose Delegated permissions, scroll down the permissions list and choose AuditLog. Select the AuditLog.Read.All checkbox. Then scroll down, choose Directory and select the Directory.Read.All checkbox. Choose User and select User.Read. Click Update permissions.
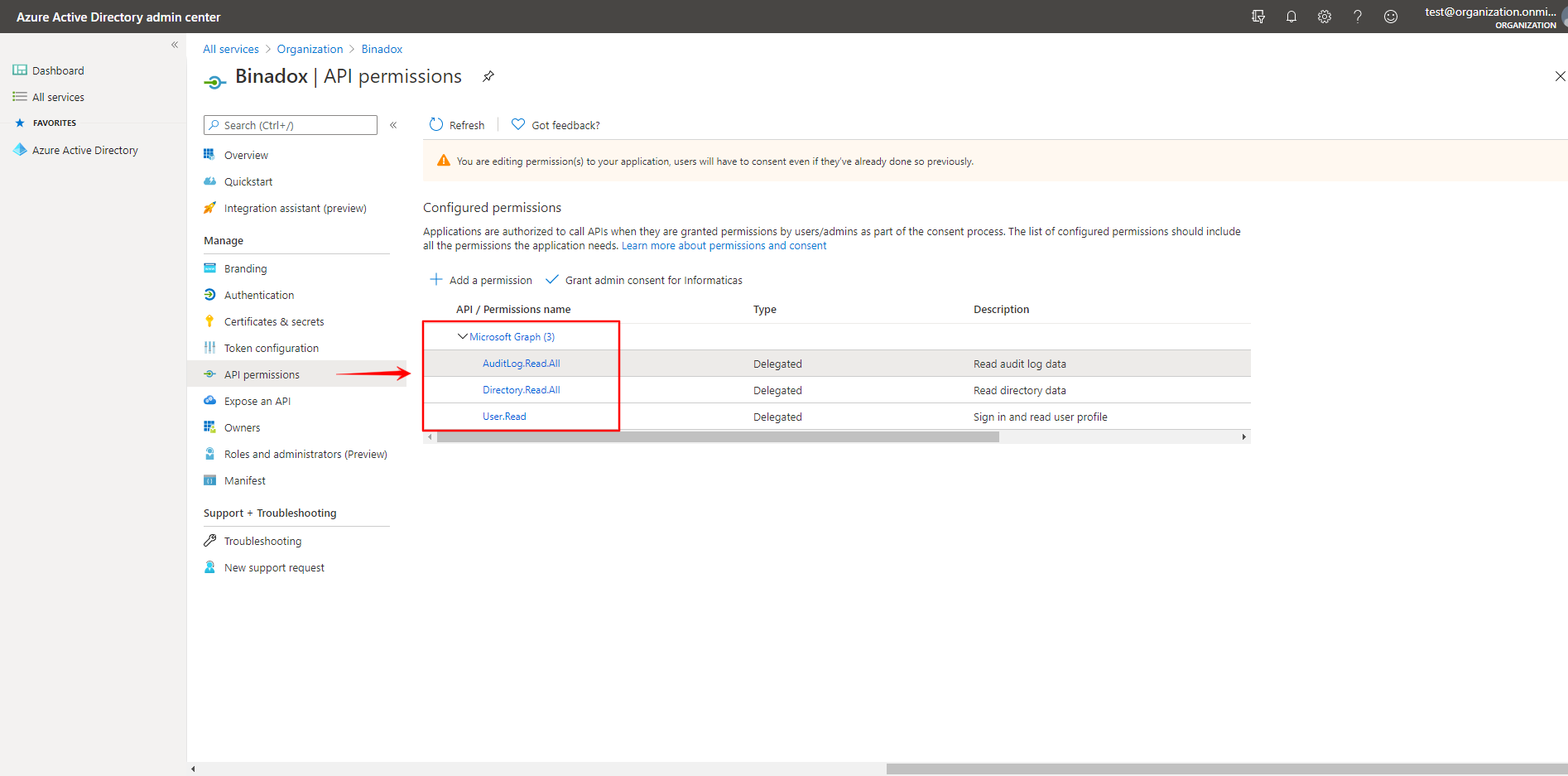
7. Under the API/Permissions name, check you configured all the required API permissions:
– AuditLog.Read.All
– Directory.Read.All
– User.Read
2.2 Add a New Office 365 User with Security Reader Permissions
For safety reasons, you may create a new user in the Microsoft 365 admin center and assign him a restricted role with limited access to your Microsoft tenant.
1. Sign in to the Microsoft 365 admin center as a global administrator.
2. In the navigation pane on the left, navigate to Users > Active users. Click on the Add a user button.
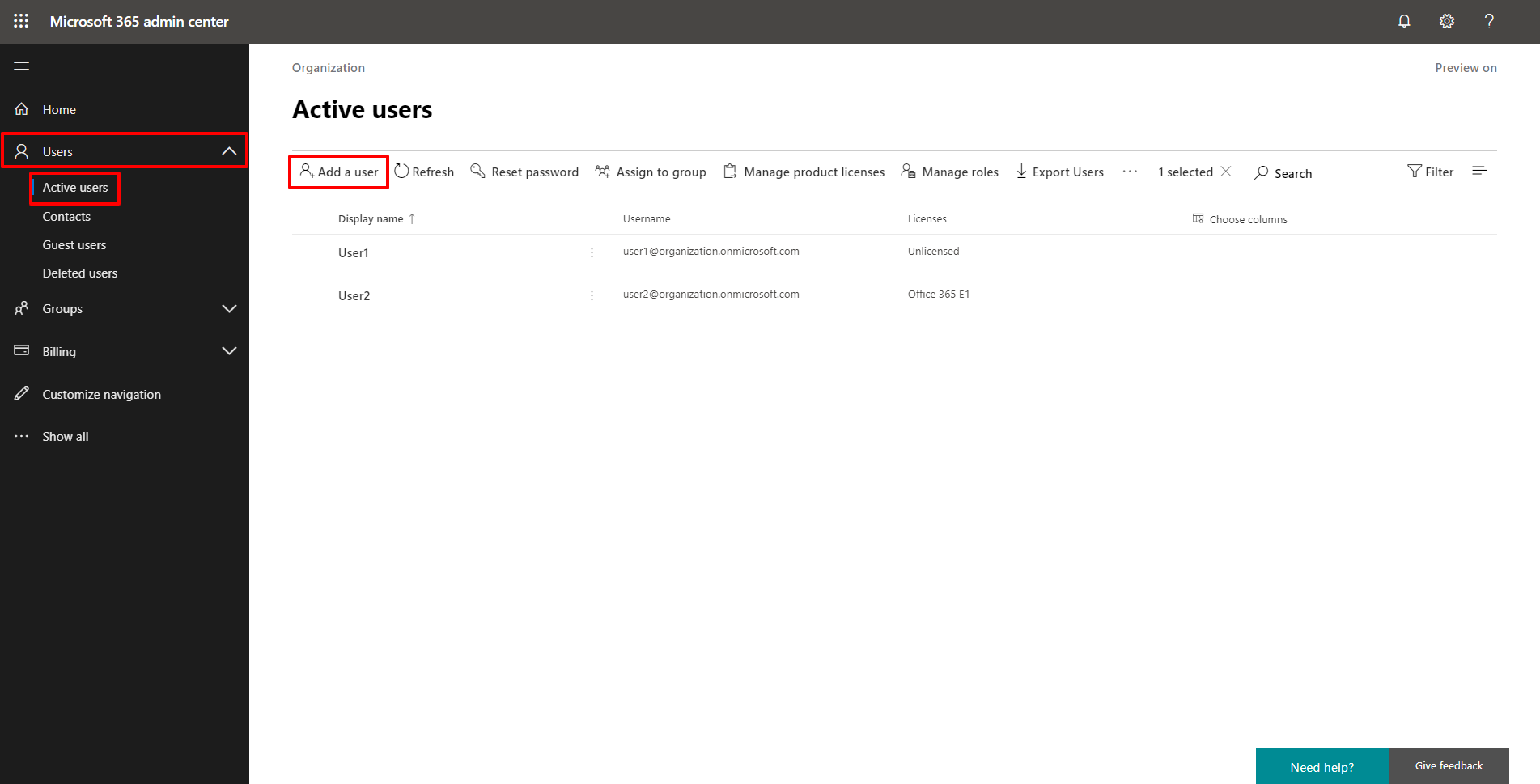
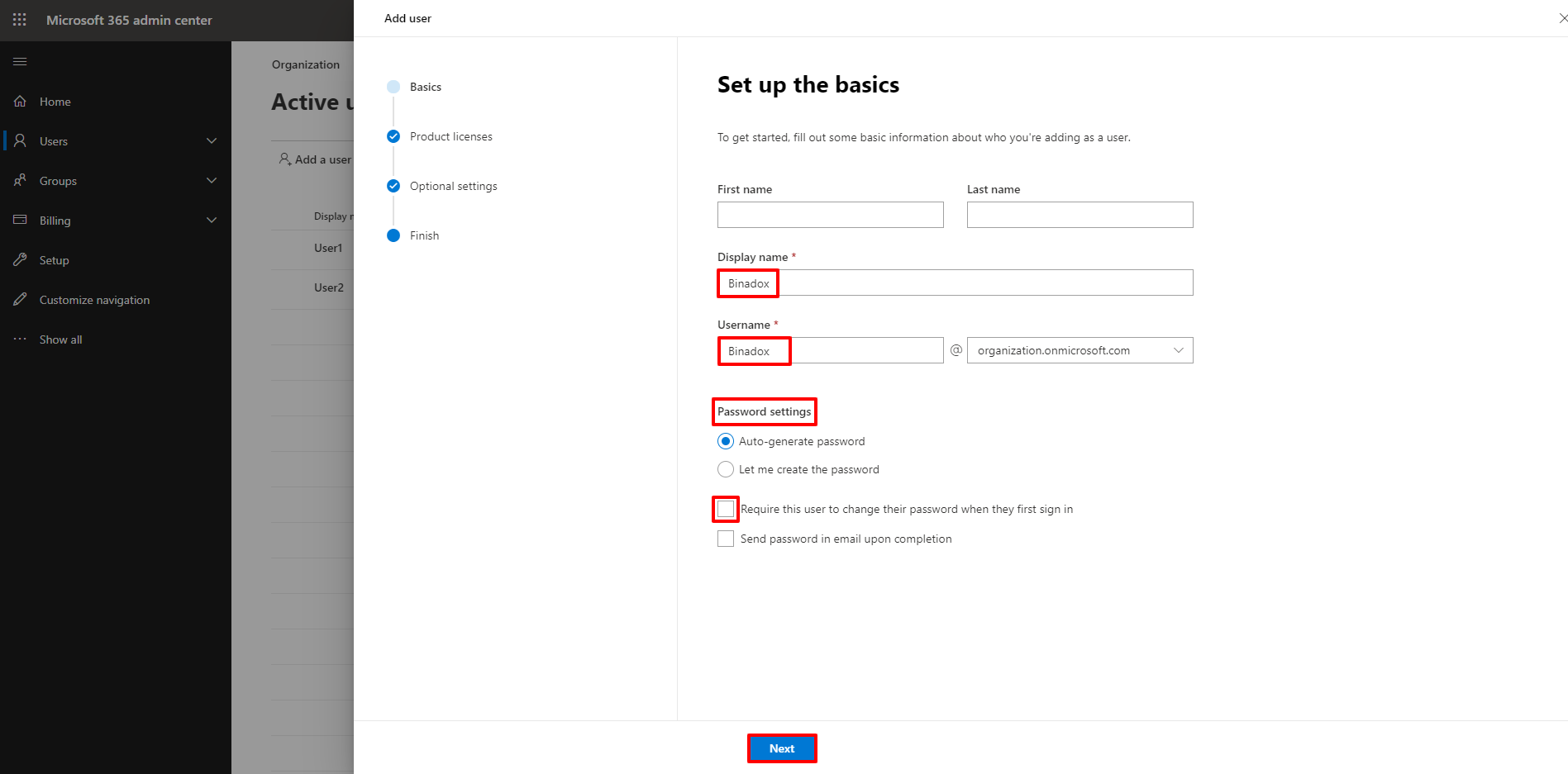
3. Fill in all the required fields in the Add user form.
– Enter a display name and a username.
– Choose the required Password settings.
– Leave Require this user to change their password when they first sign in unchecked (so you do not have to log in to the Azure portal as a new user and create a new password to activate the account).
Click Next.
4. In the Product licenses view, select the location. Select the Create user without product license option. Click Next.
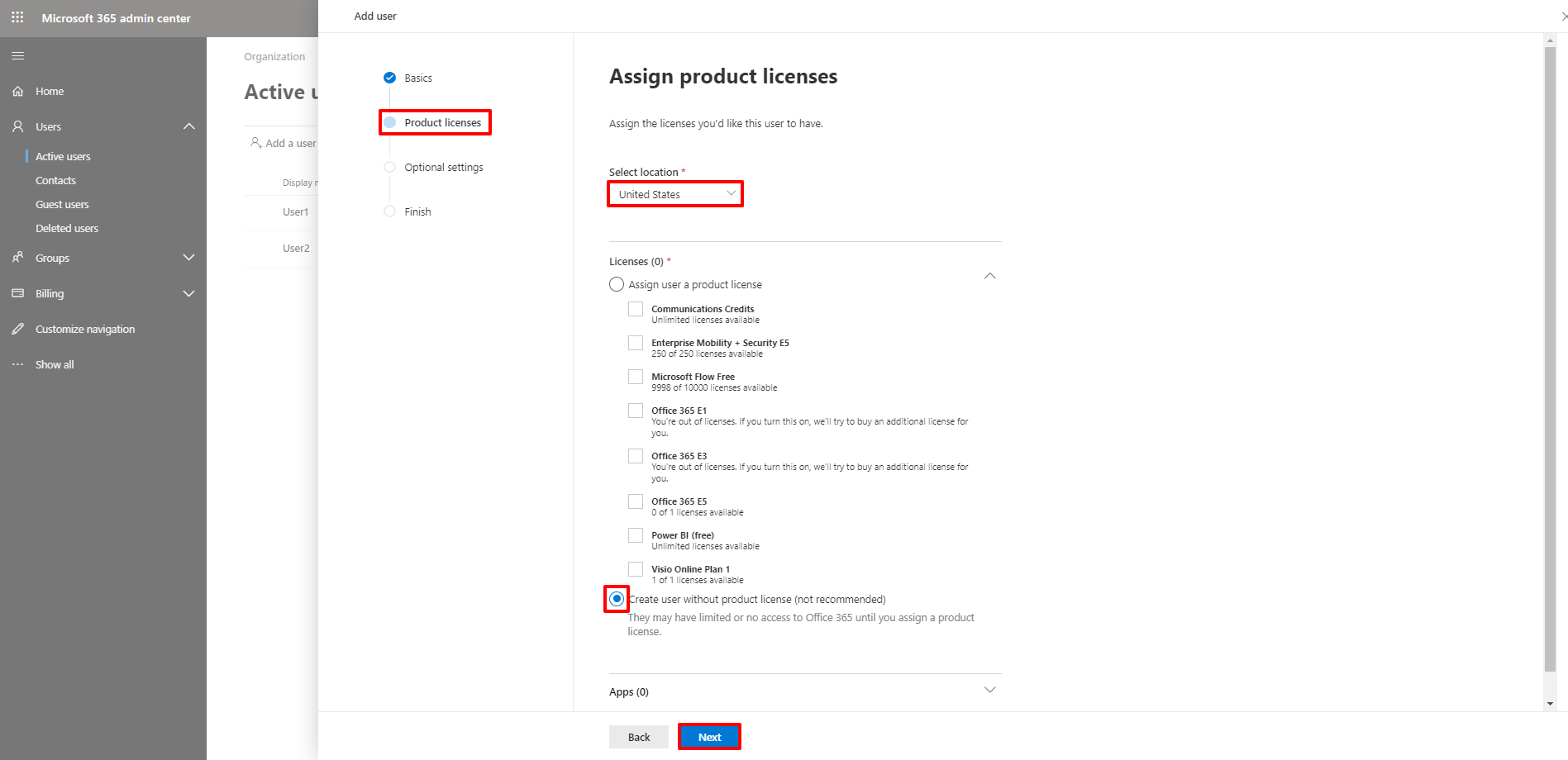
5. In the Optional settings view, click Roles. Select Admin center access. Click Show all by category.
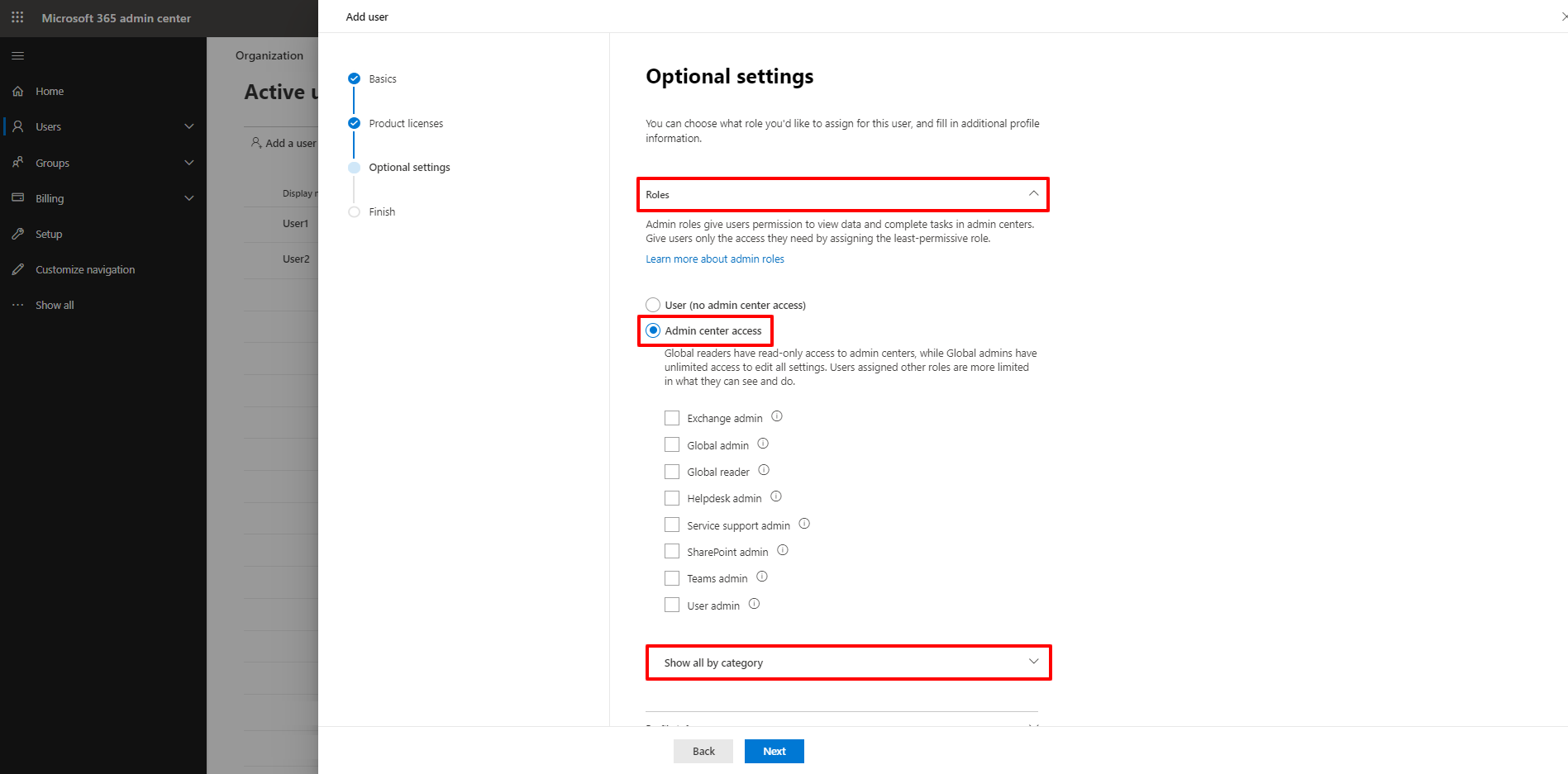
6. Scroll down to the Other category. Select the Billing admin checkbox. Click Next.
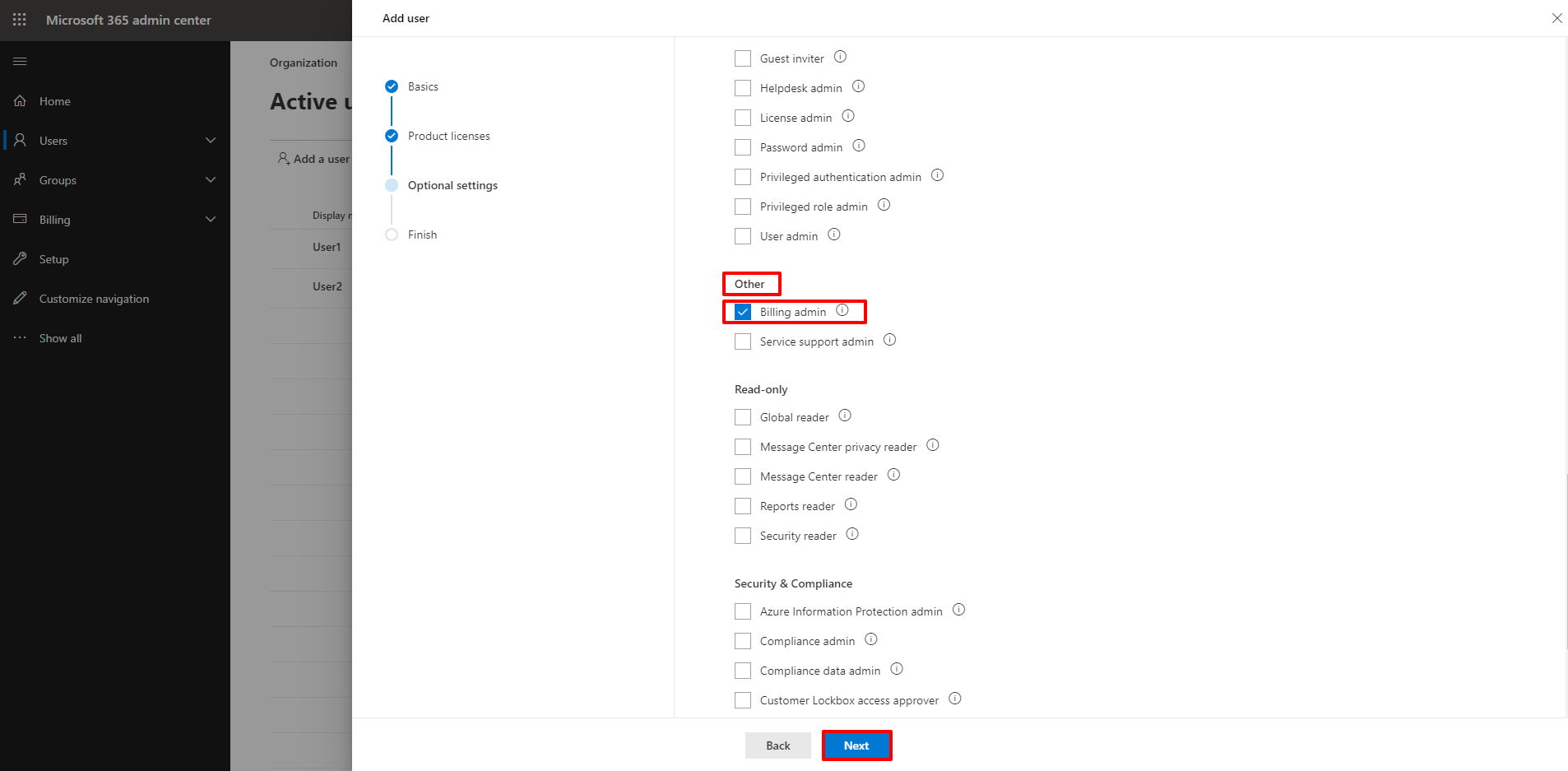
7.Review data and click Finish adding to add a new user.
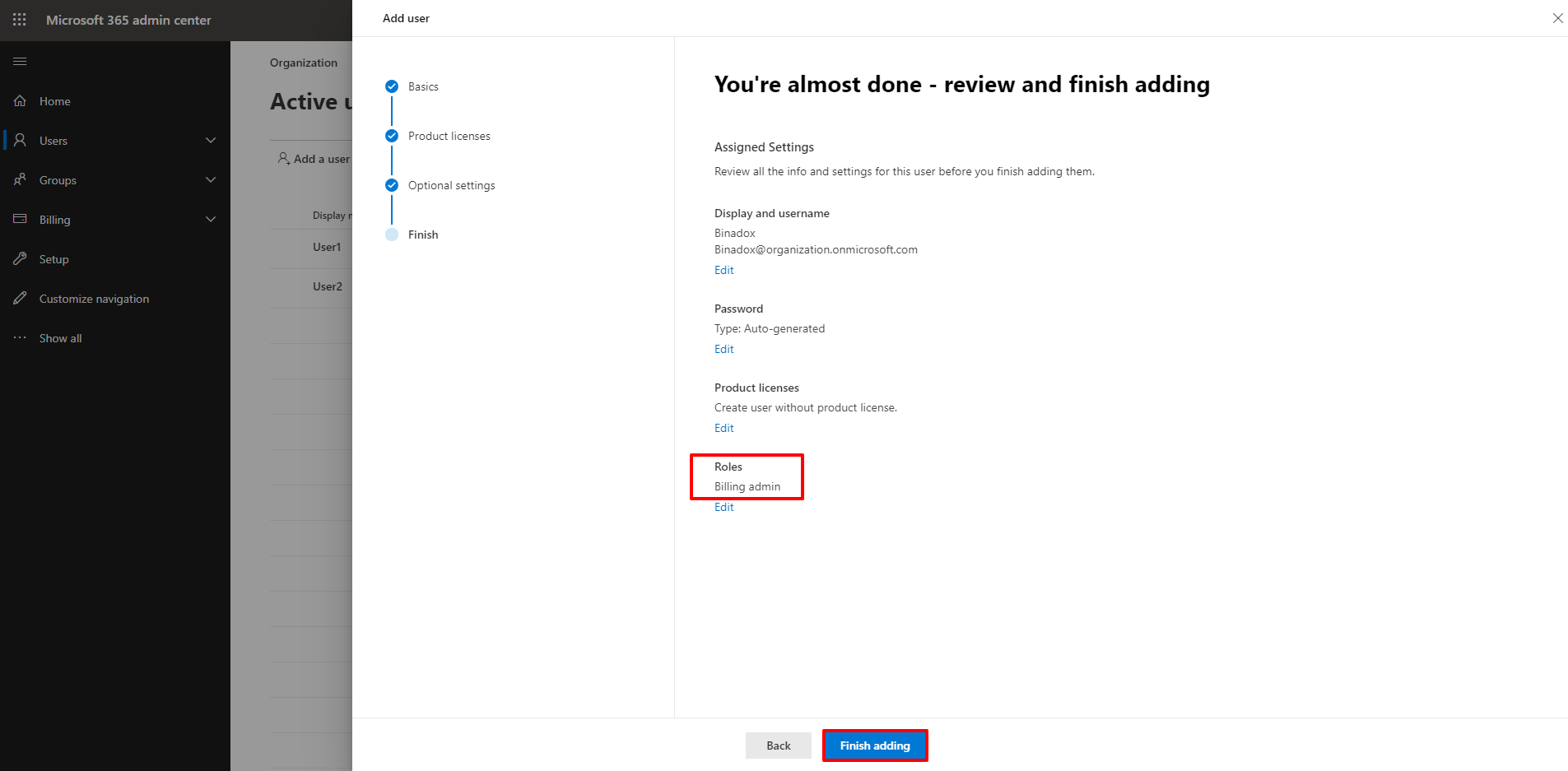
8. Copy a username and a password. Click Close.
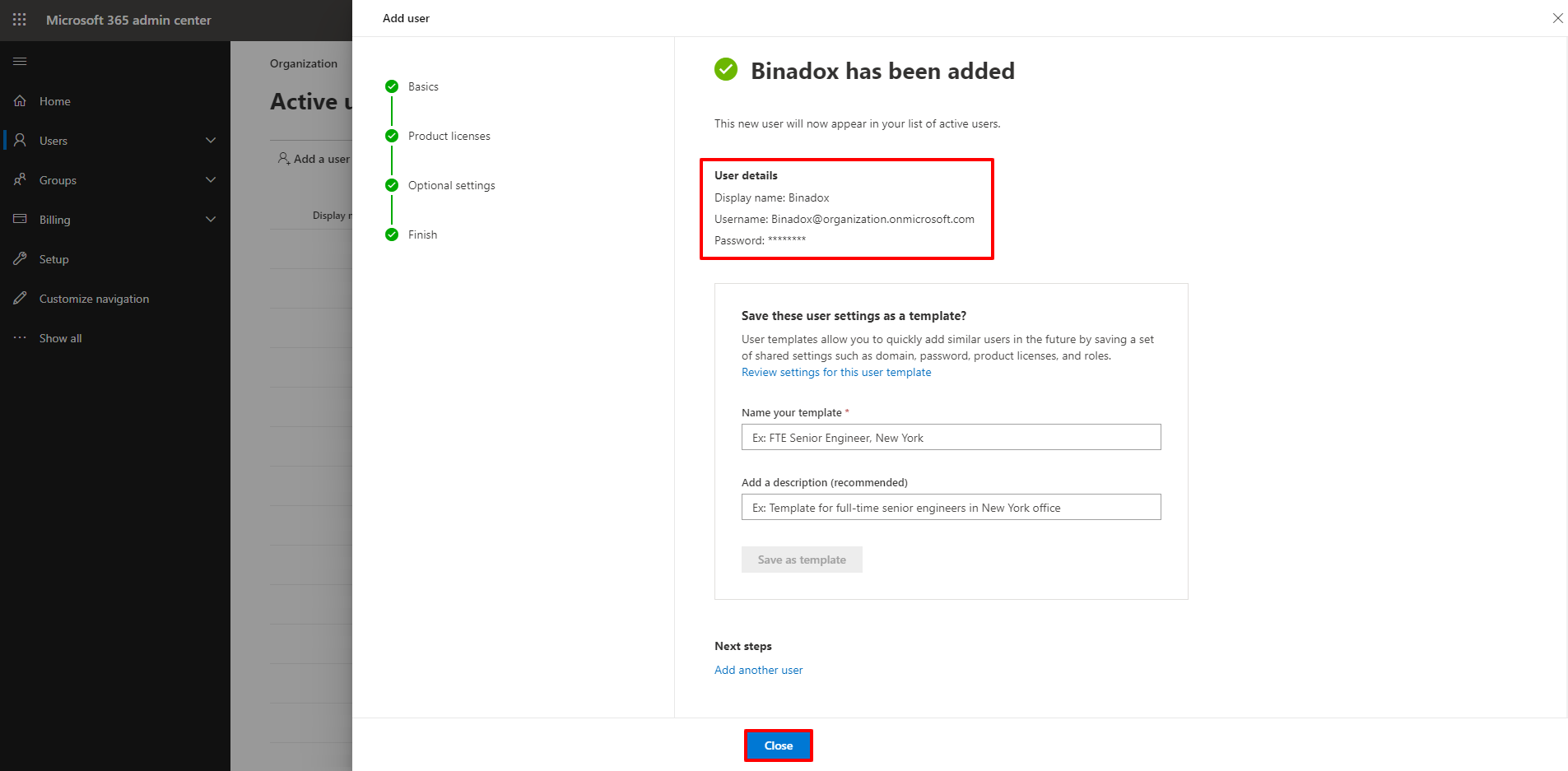
9. To specify the permission levels of the new user, click …Show all in the navigation pane on the left to open up the Admin centers section. Go to Security & Compliance.
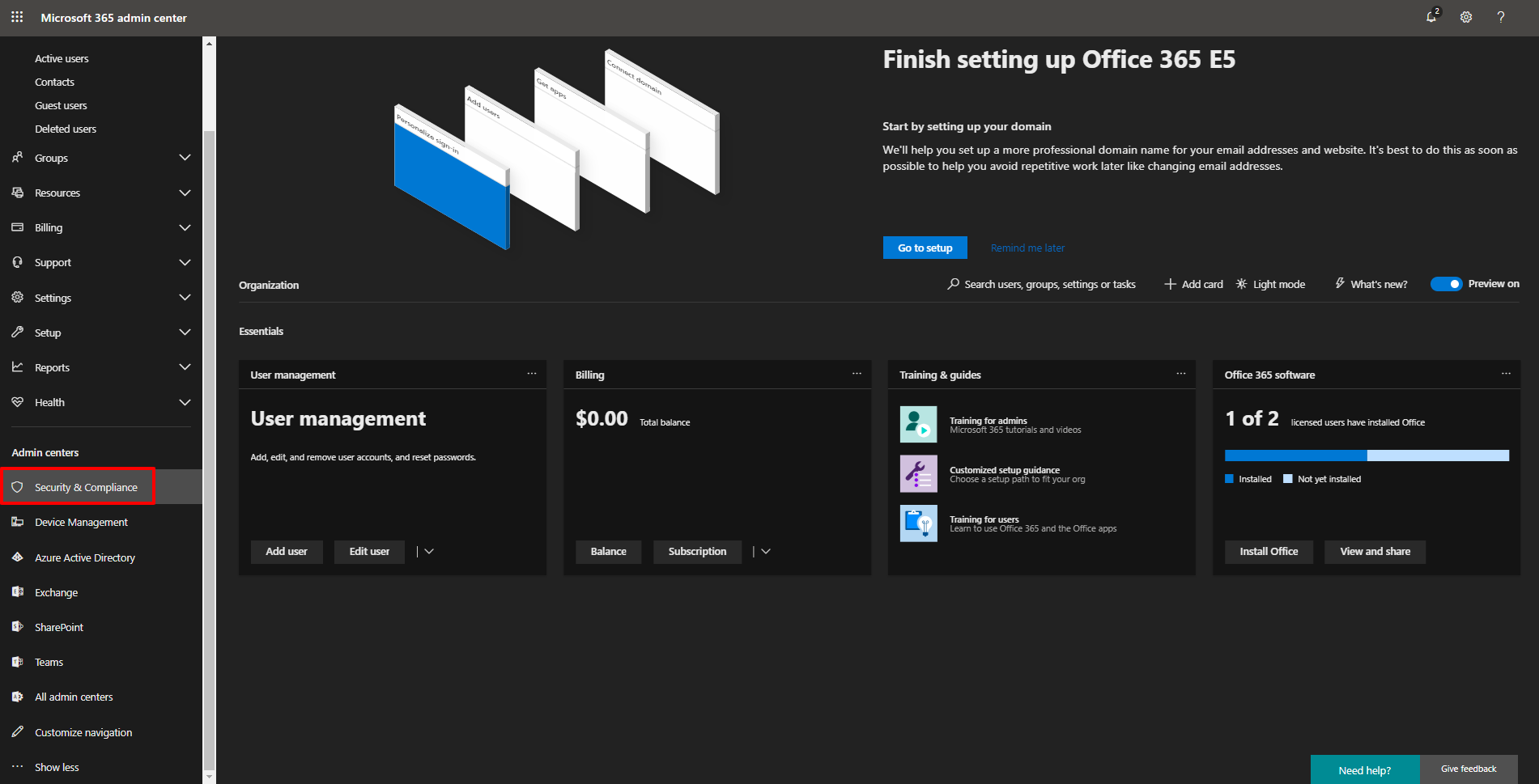
10. You will be redirected to the Office 365 Security & Compliance dashboard. In the navigation pane on the left, click Permissions. Select the Security Reader check-box in the list of role group names. In the Security Reader view that opens on the right, go to Members and click Edit.
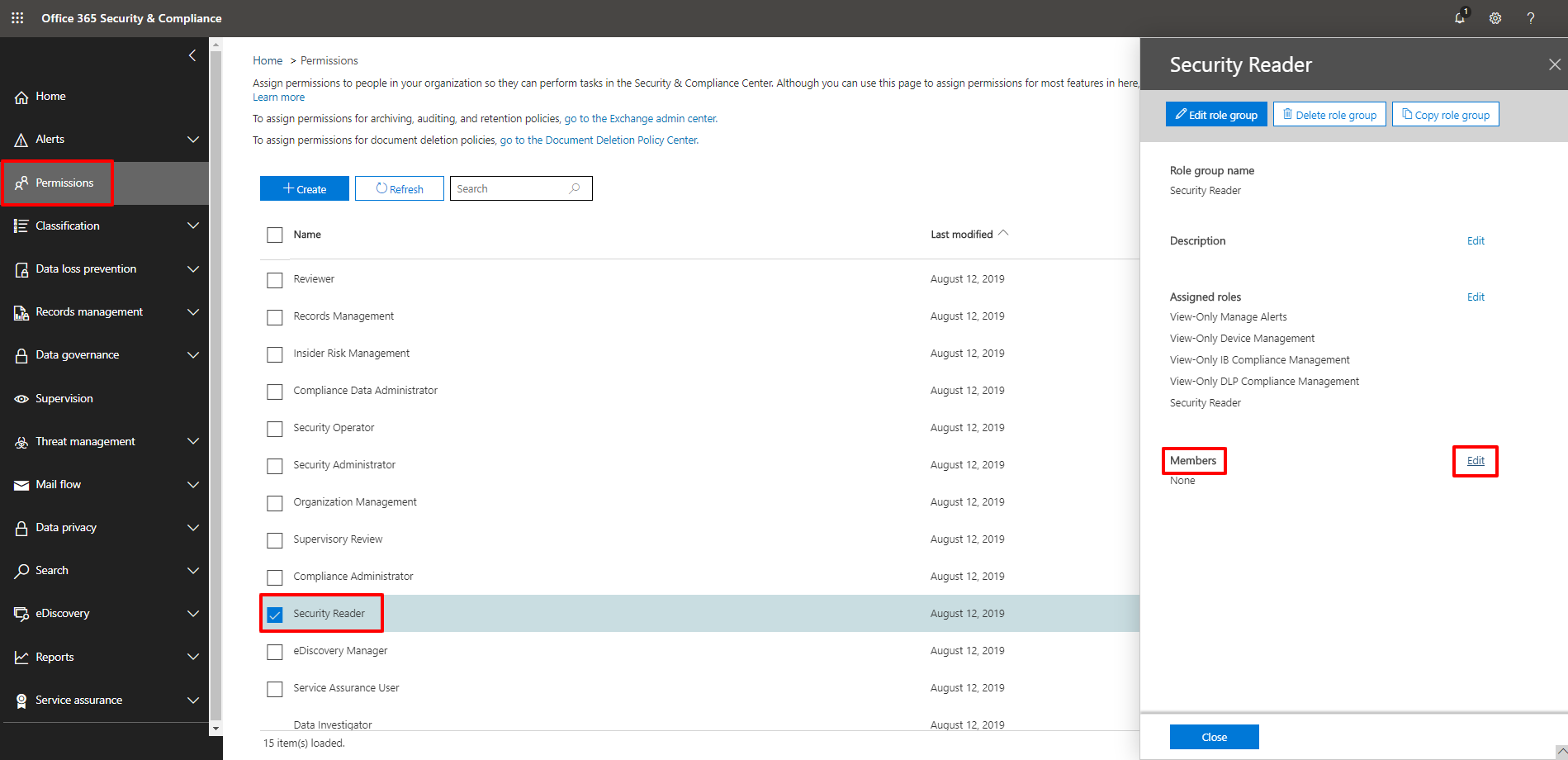
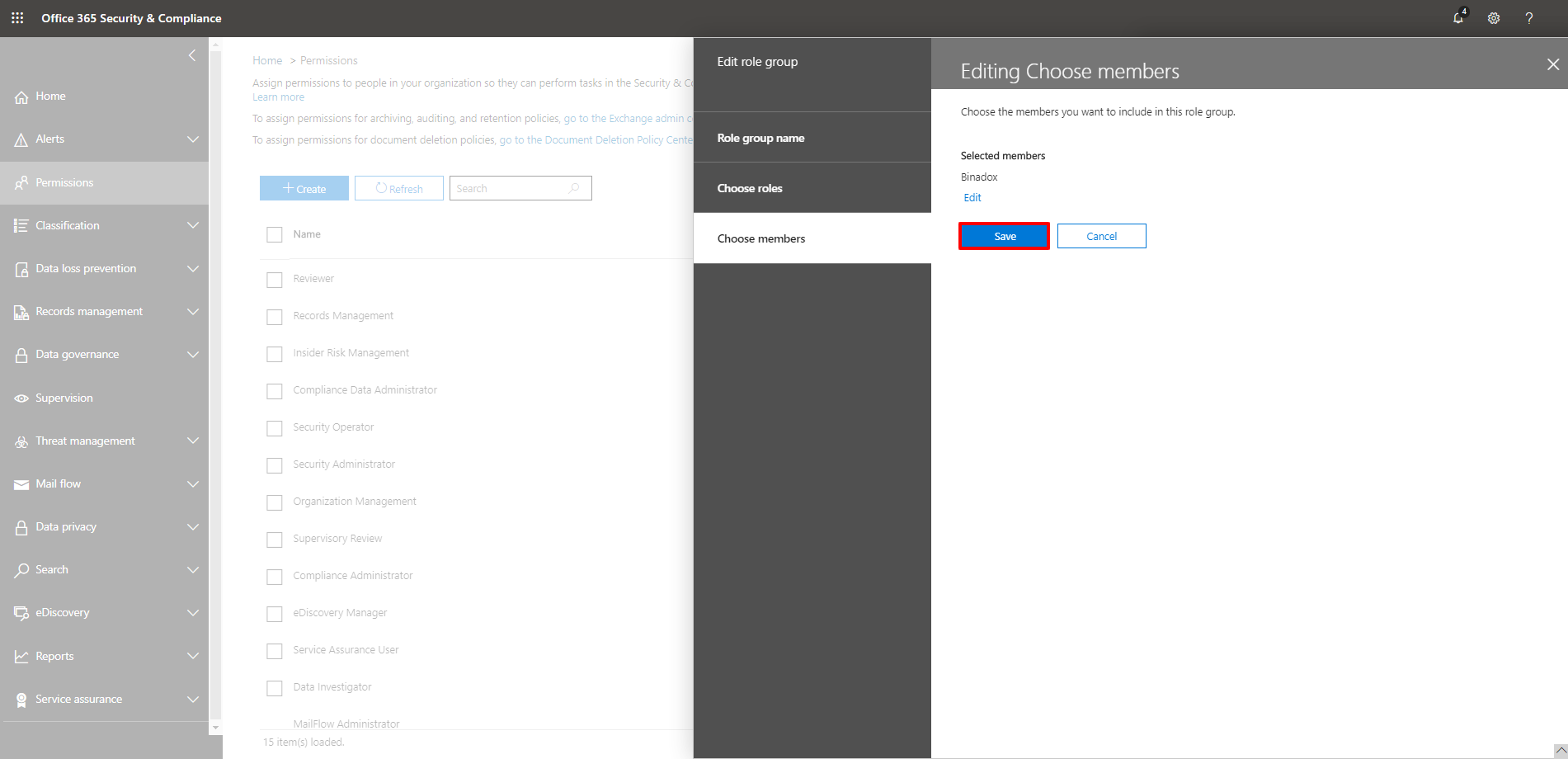
11. In the Editing Choose members view, click Choose members.
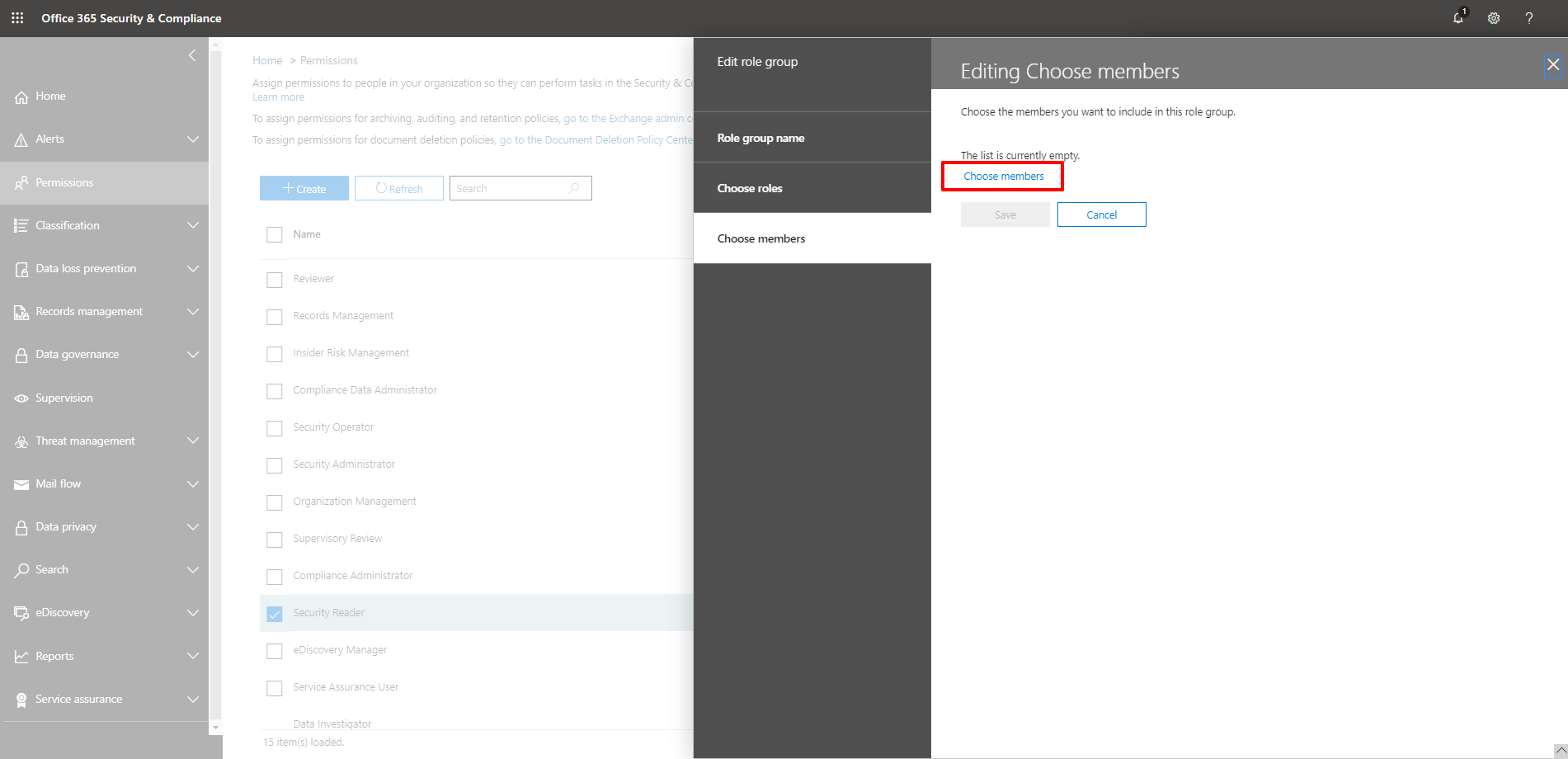
12. In the Choose members view, click the + Add button to add the new user to the Security Reader role group.
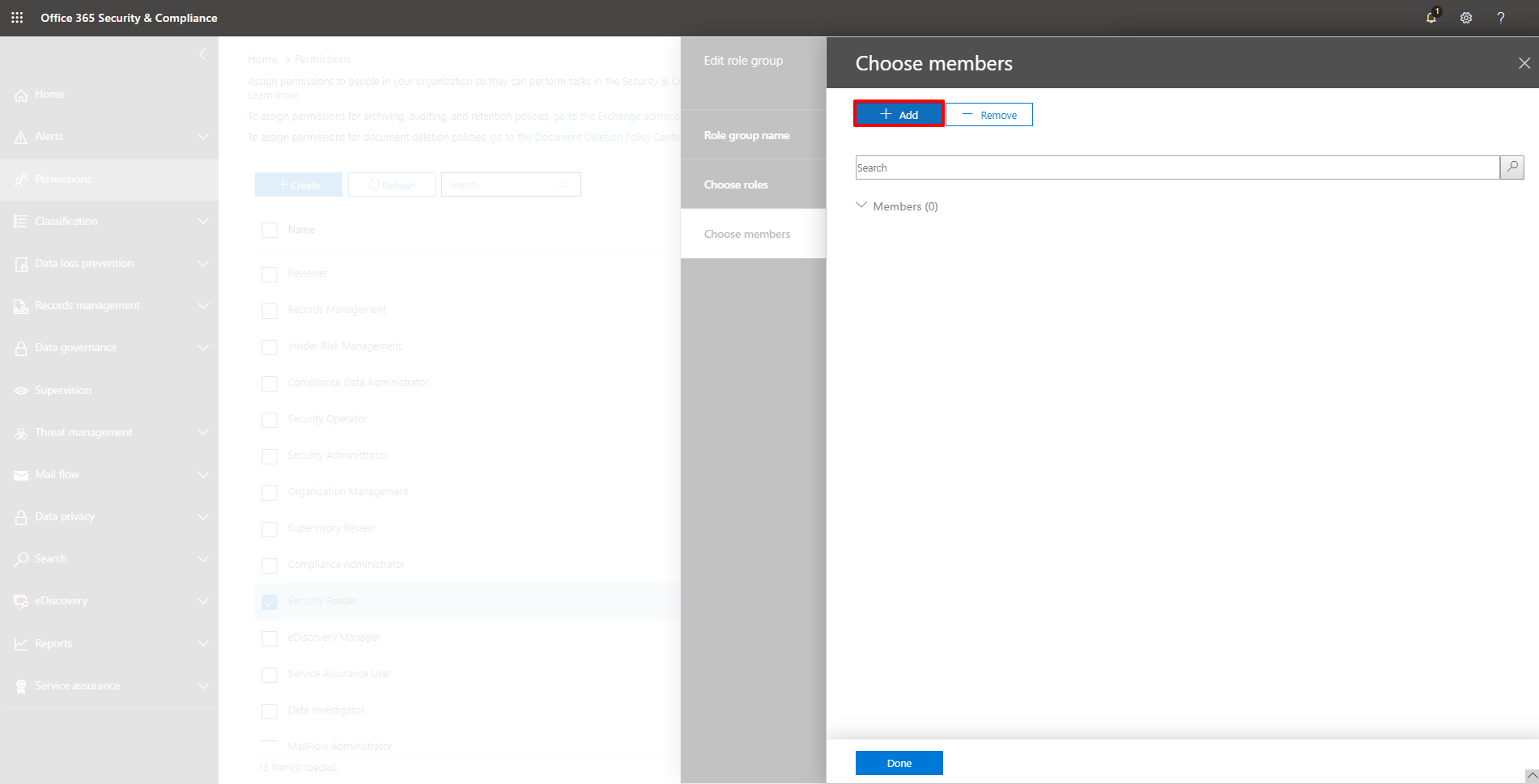
13. Select the new user from the Members list. Use the search box, if necessary. Click Add.
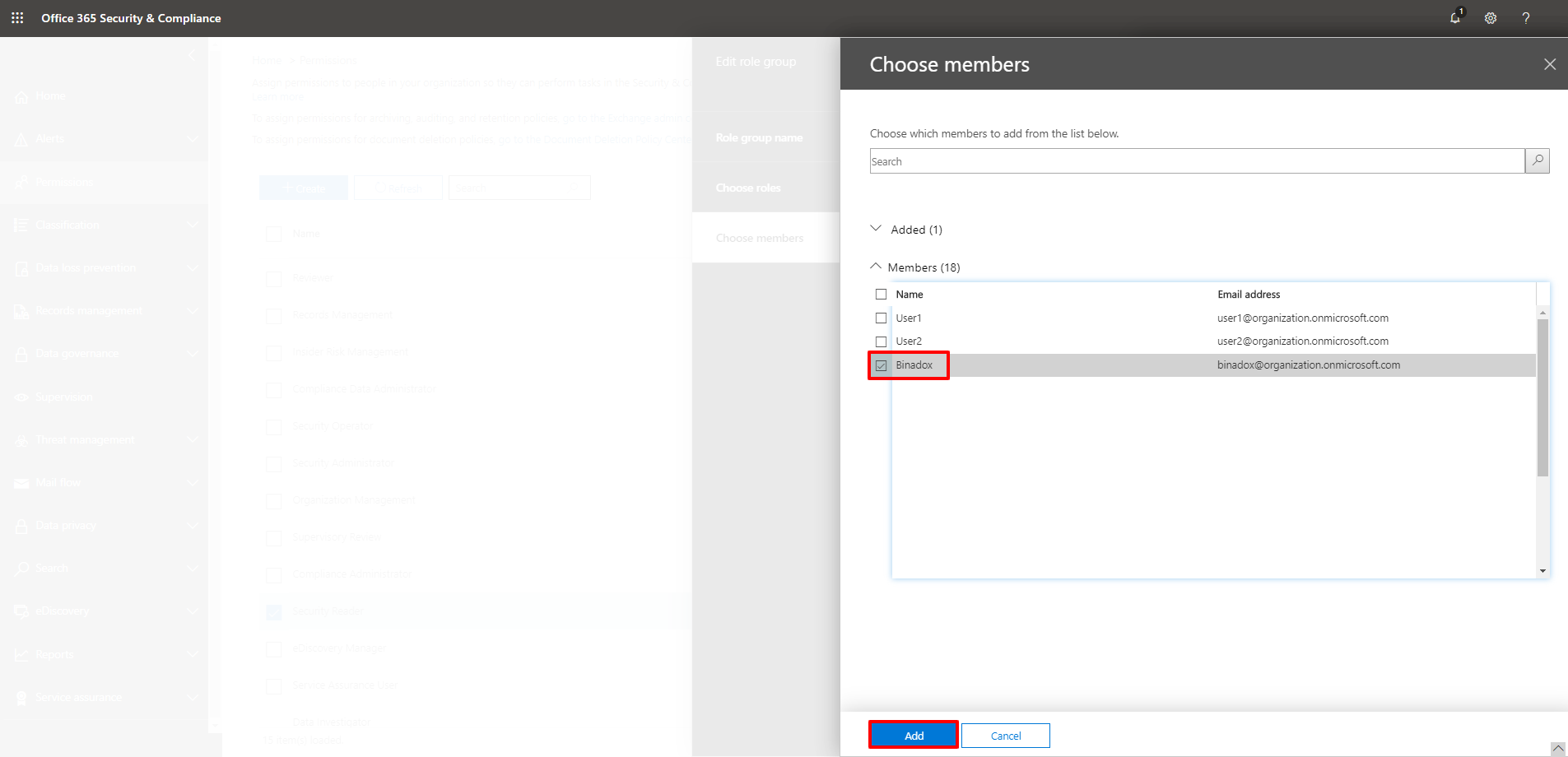
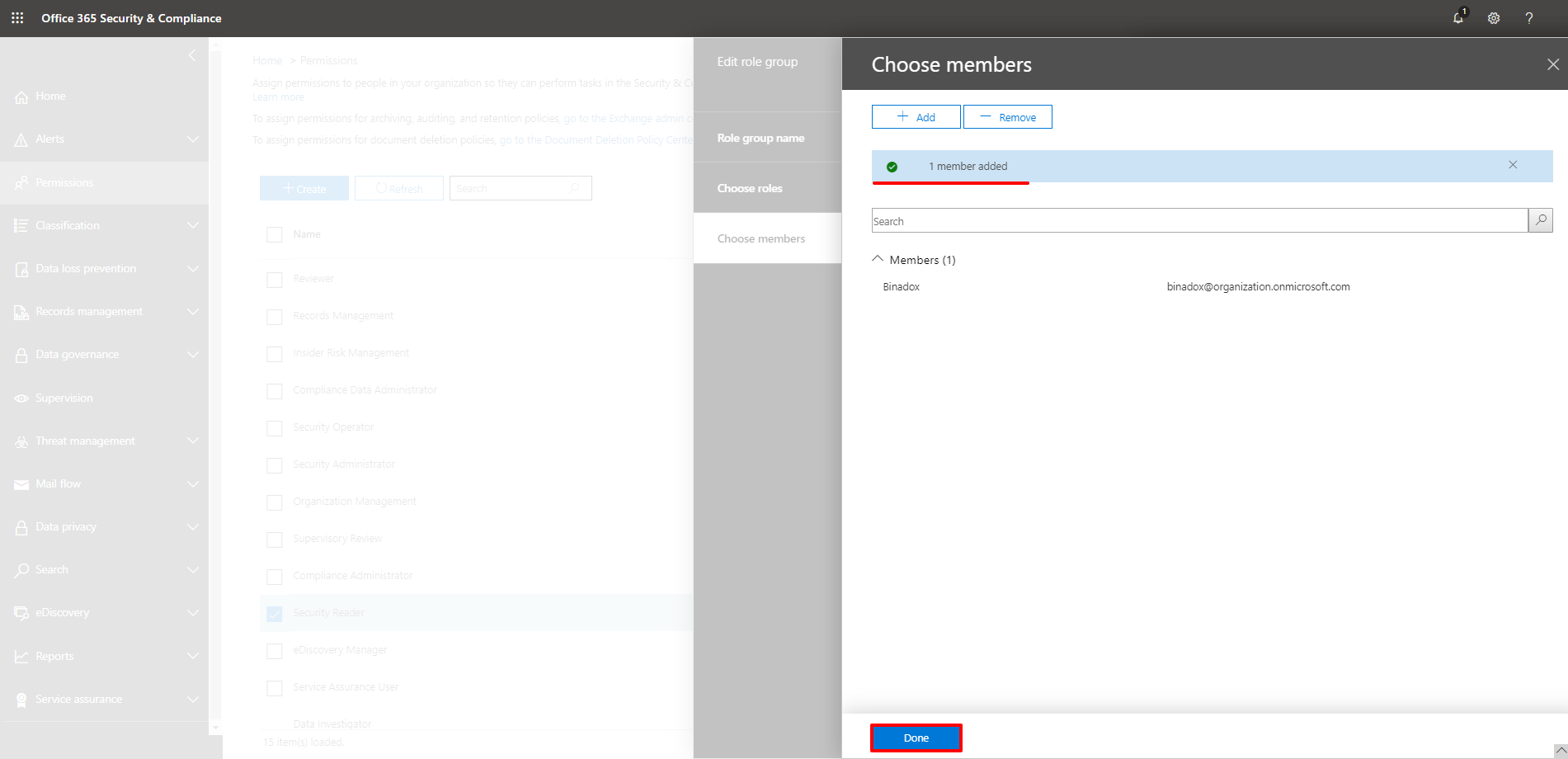
14. Click Done to add the user to the Security Reader role group.
2.3 Disable Multi-Factor Authentication
Multi-Factor Authentication enabled for the user may disrupt the connection with Binadox. To disable it, do the following:
1. Log into the Microsoft Azure portal as a global administrator. In the navigation pane on the left, go to Azure Active Directory > Users.
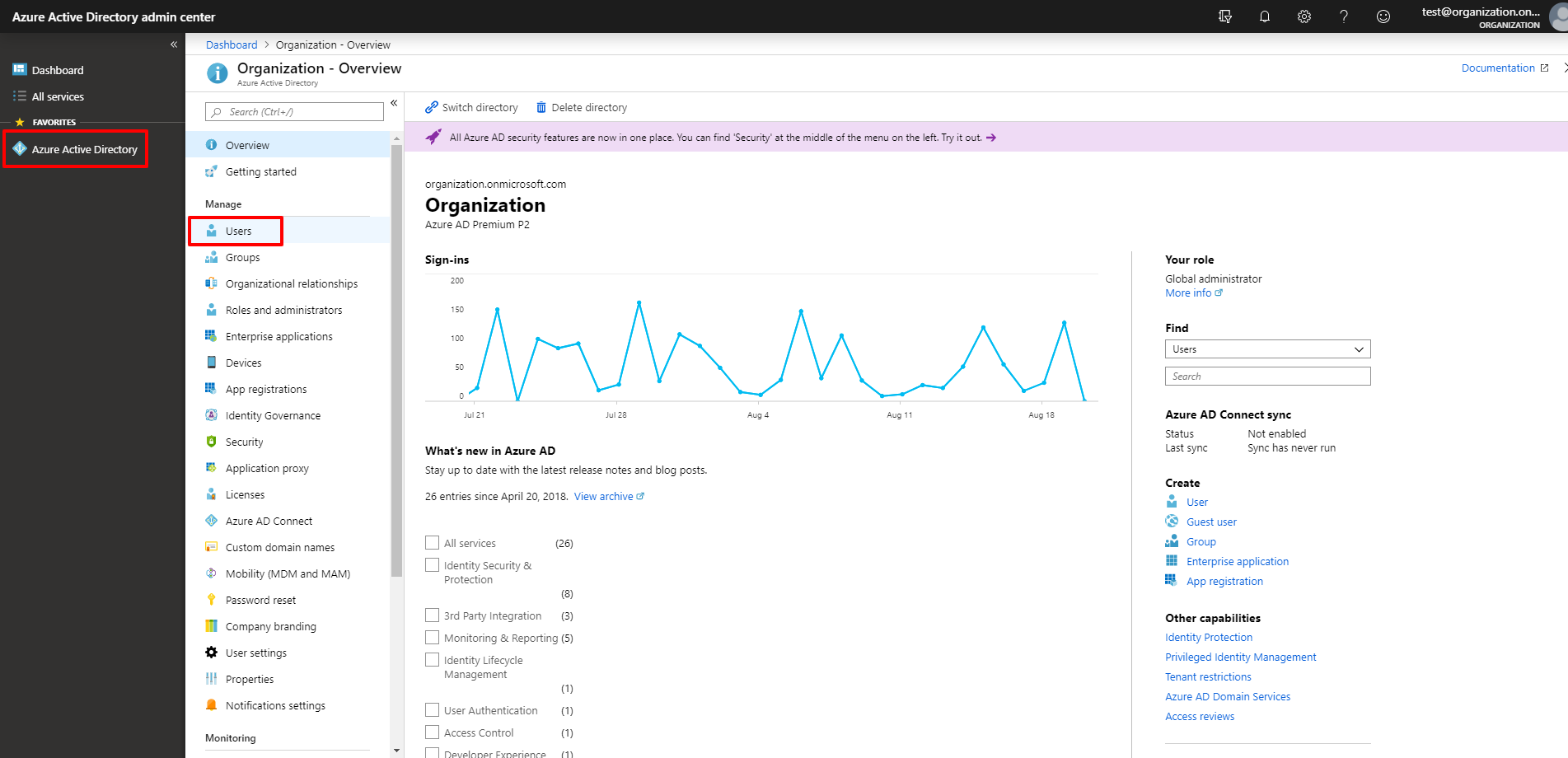
2. Click All users in the navigation pane. In the All Users view, click Multi-Factor Authentication on the toolbar.
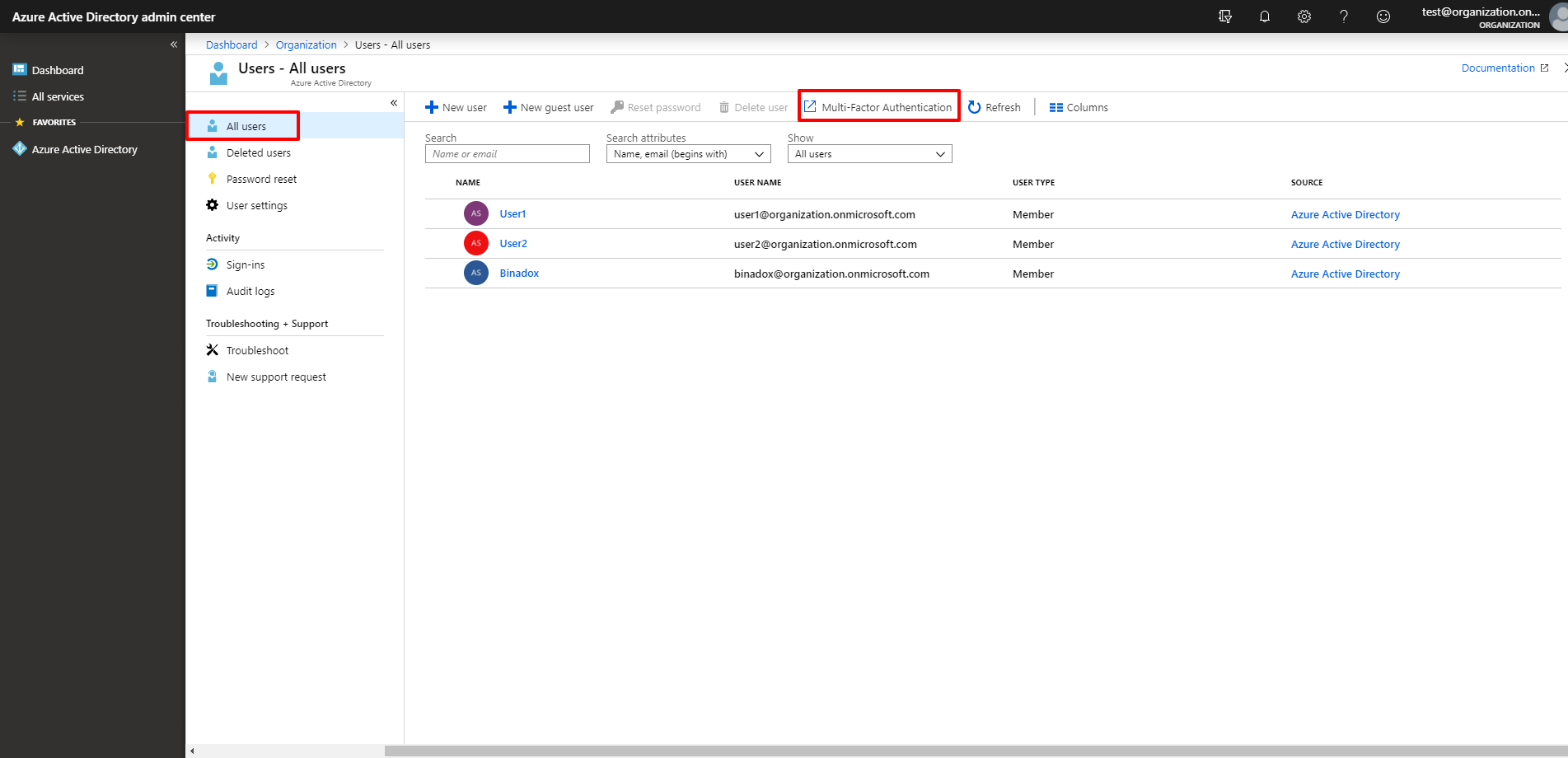
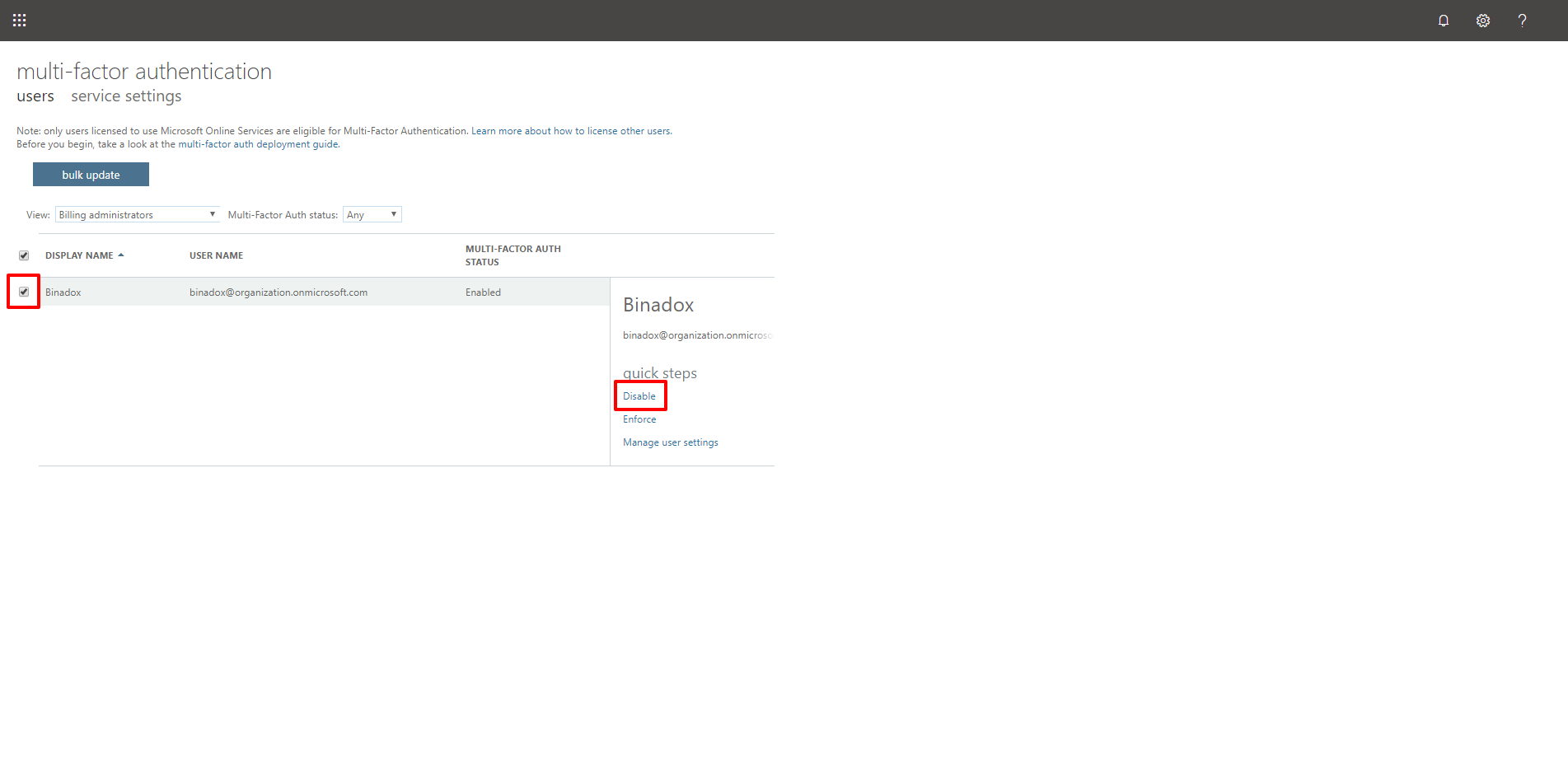
3. You will be redirected to the Multi-Factor Authentication view. Put the tick mark next to the name of the required user. In the appeared menu to the right, click the Disable option in the Quick Steps section. Click Yes in the appeared window to confirm the action.
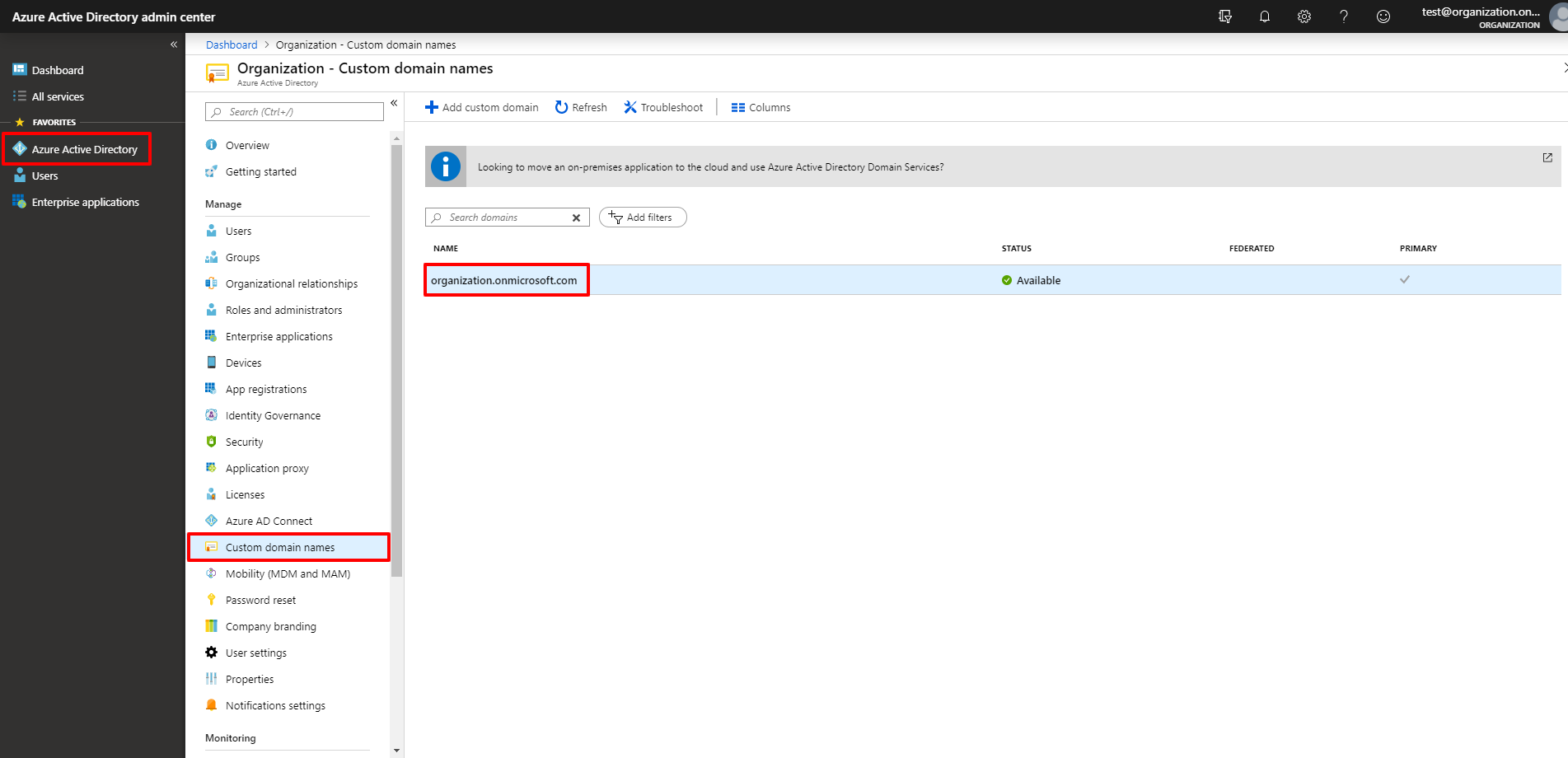
2.4 Locate Integration Data on the Azure Portal
1. To find the Tenant domain, Application ID and Client Secret, sign in to the Microsoft Azure portal as a global administrator. Navigate to Azure Active Directory.
2. To locate the Tenant domain, click Custom domain names. Copy your tenant domain from the Name field (e.g. organization.onmicrosoft.com). You may also hover the mouse pointer over the profile information at the top right corner of the menu bar to see the tenant domain.
3. To locate an Application (client) ID, click Azure Active Directory > App registrations in the navigation pane on the left. Click on the name of the Binadox application. To quickly locate it, type in its name in the search bar.
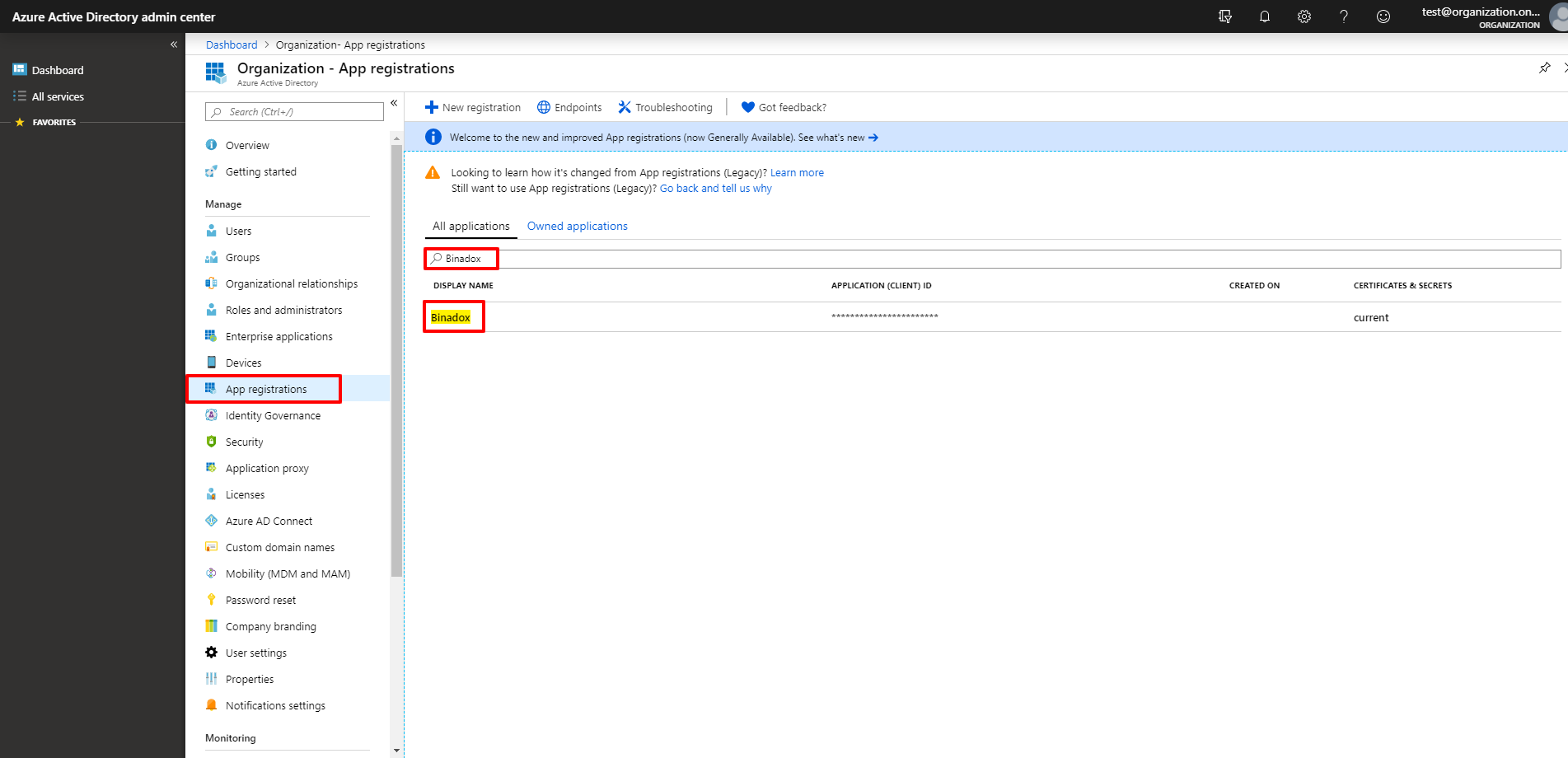
4. To copy an Application (client) ID, hover the mouse pointer over the value. Click on the appeared icon to copy it to the clipboard.
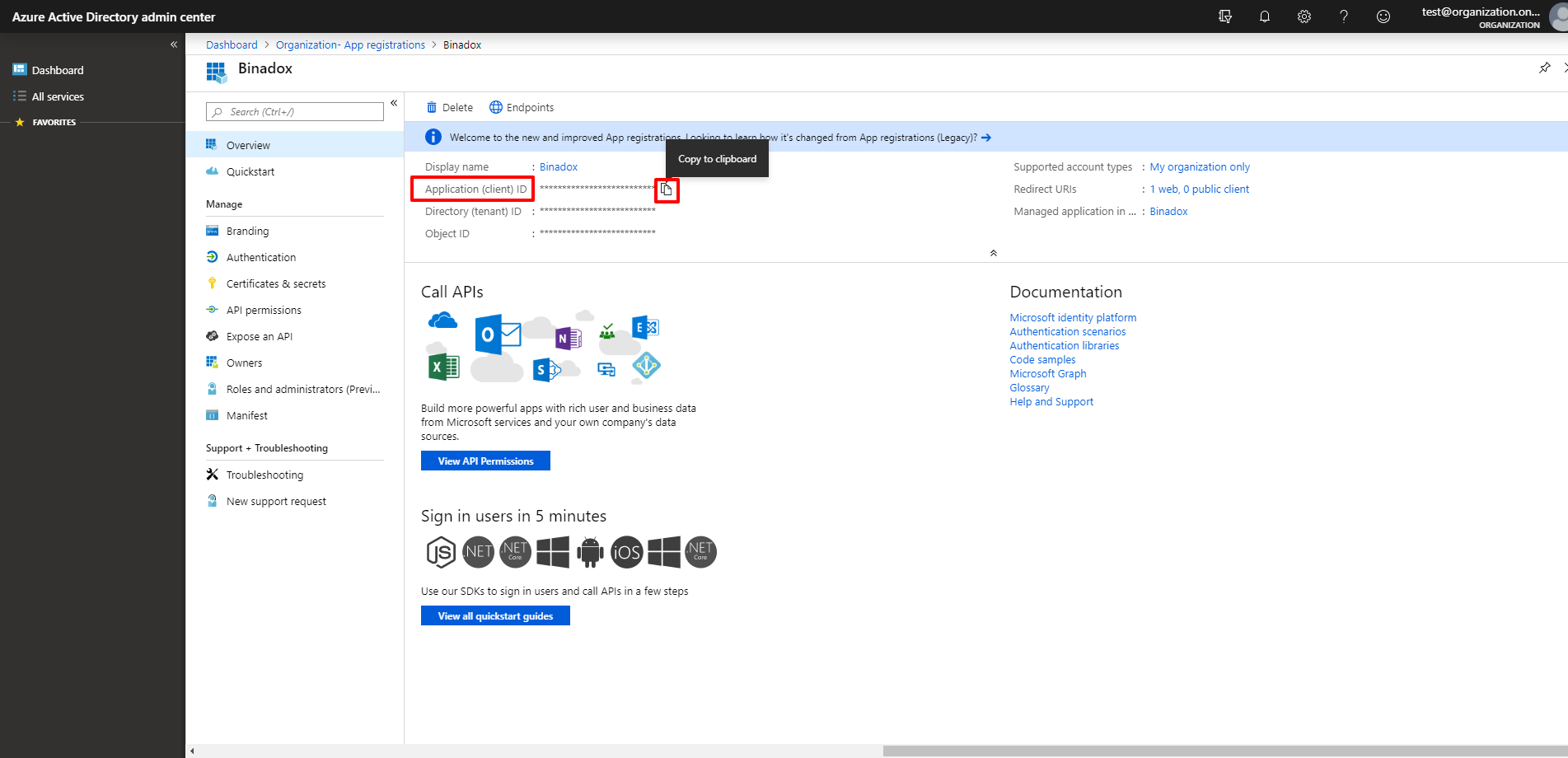
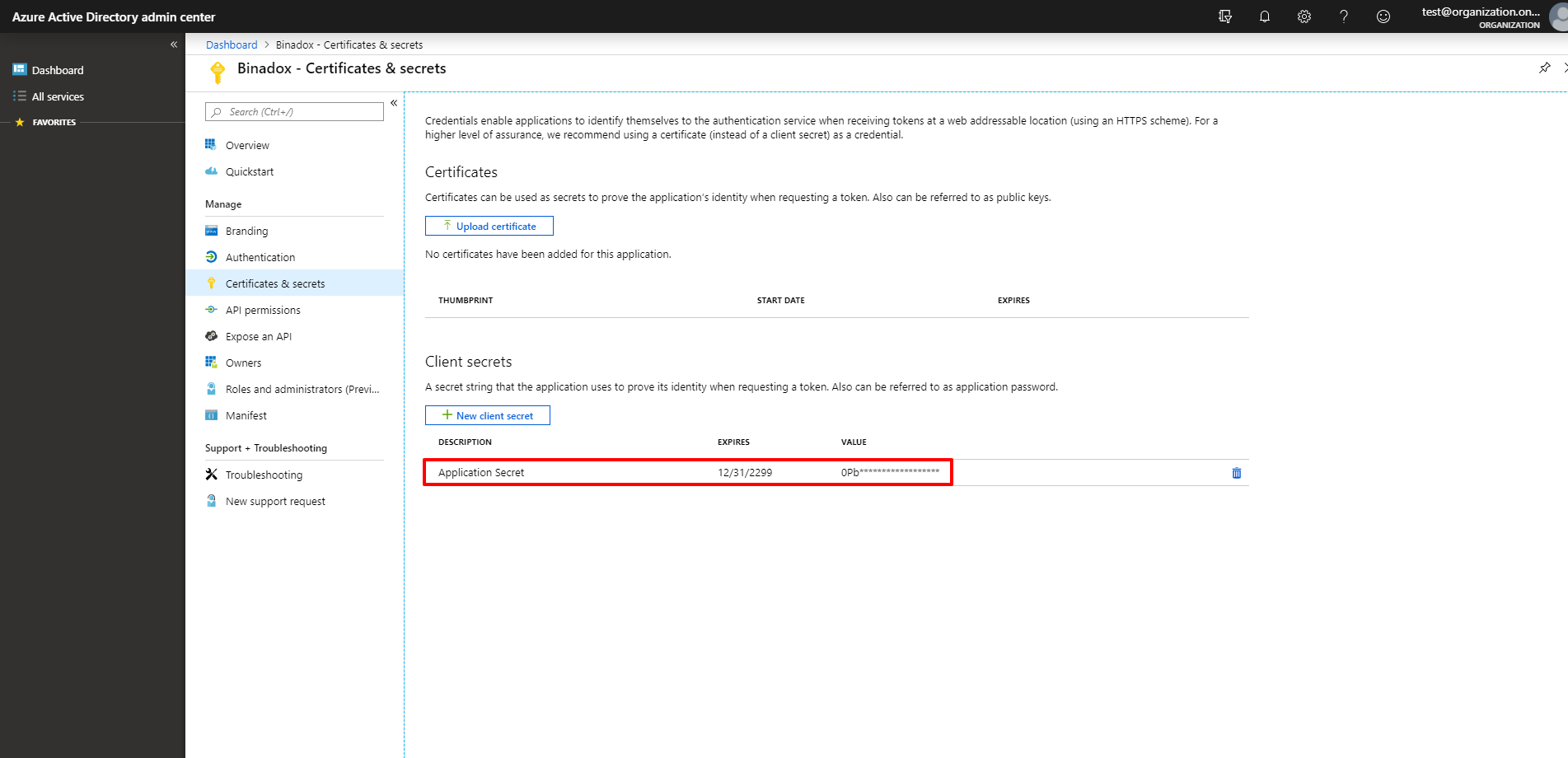
5. To generate a new Client Secret, go to the Certificates and secrets section and click the New client secret button.
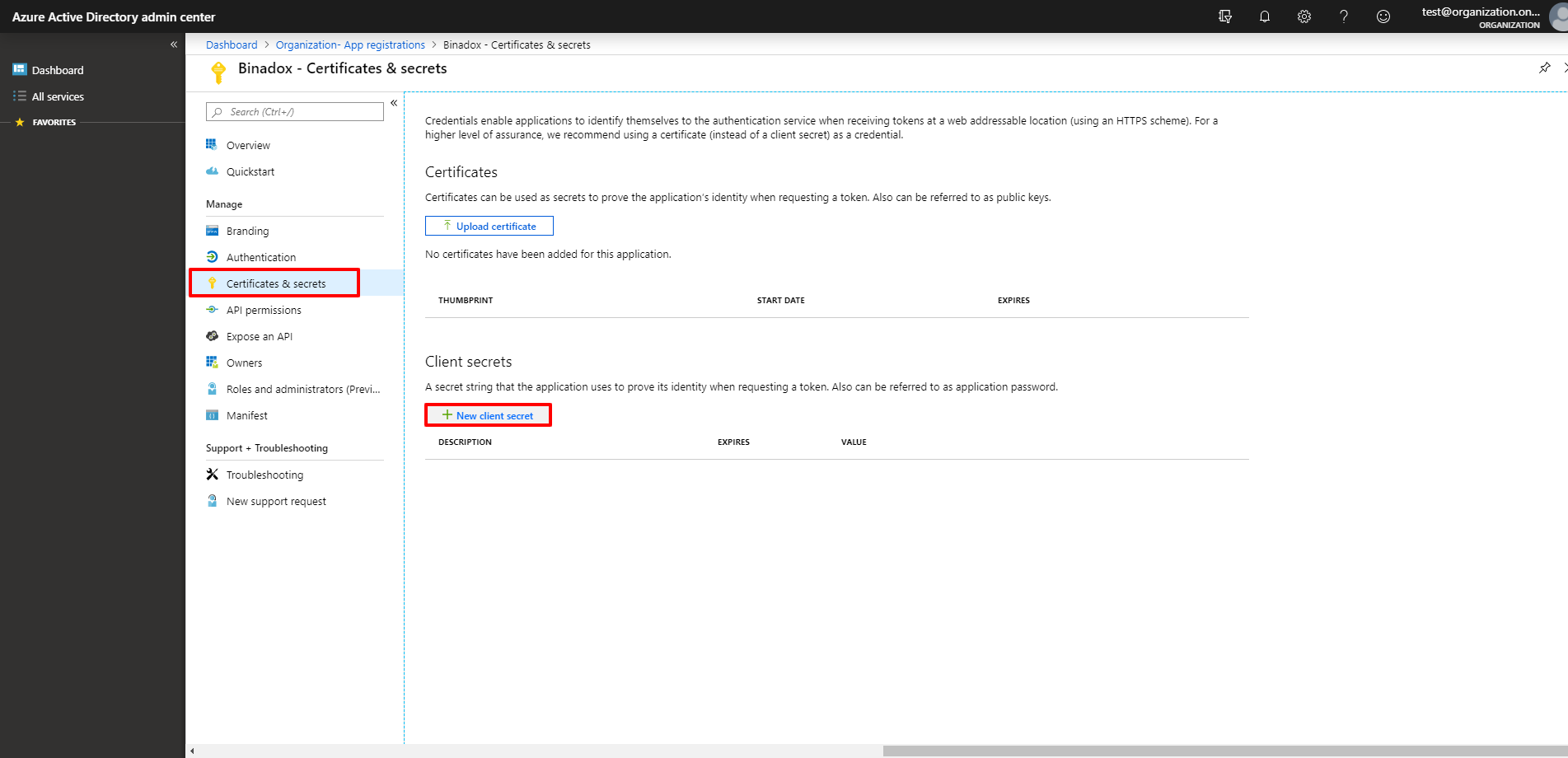
6. Make a Description for your client secret, select its duration in the Expires section and click the Add button.
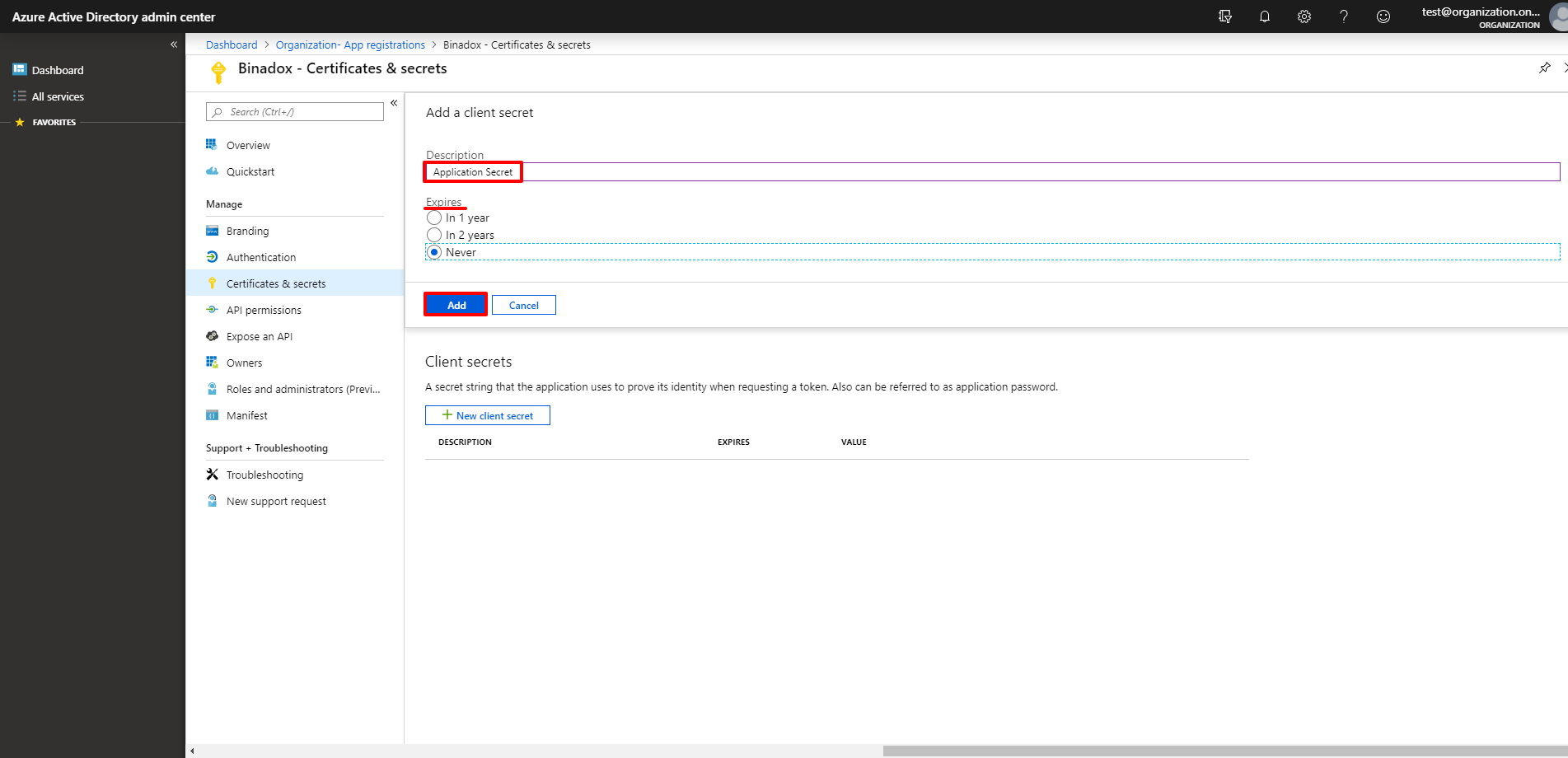
7. Hover the mouse pointer over the value and click on the appeared icon to copy it to the clipboard.
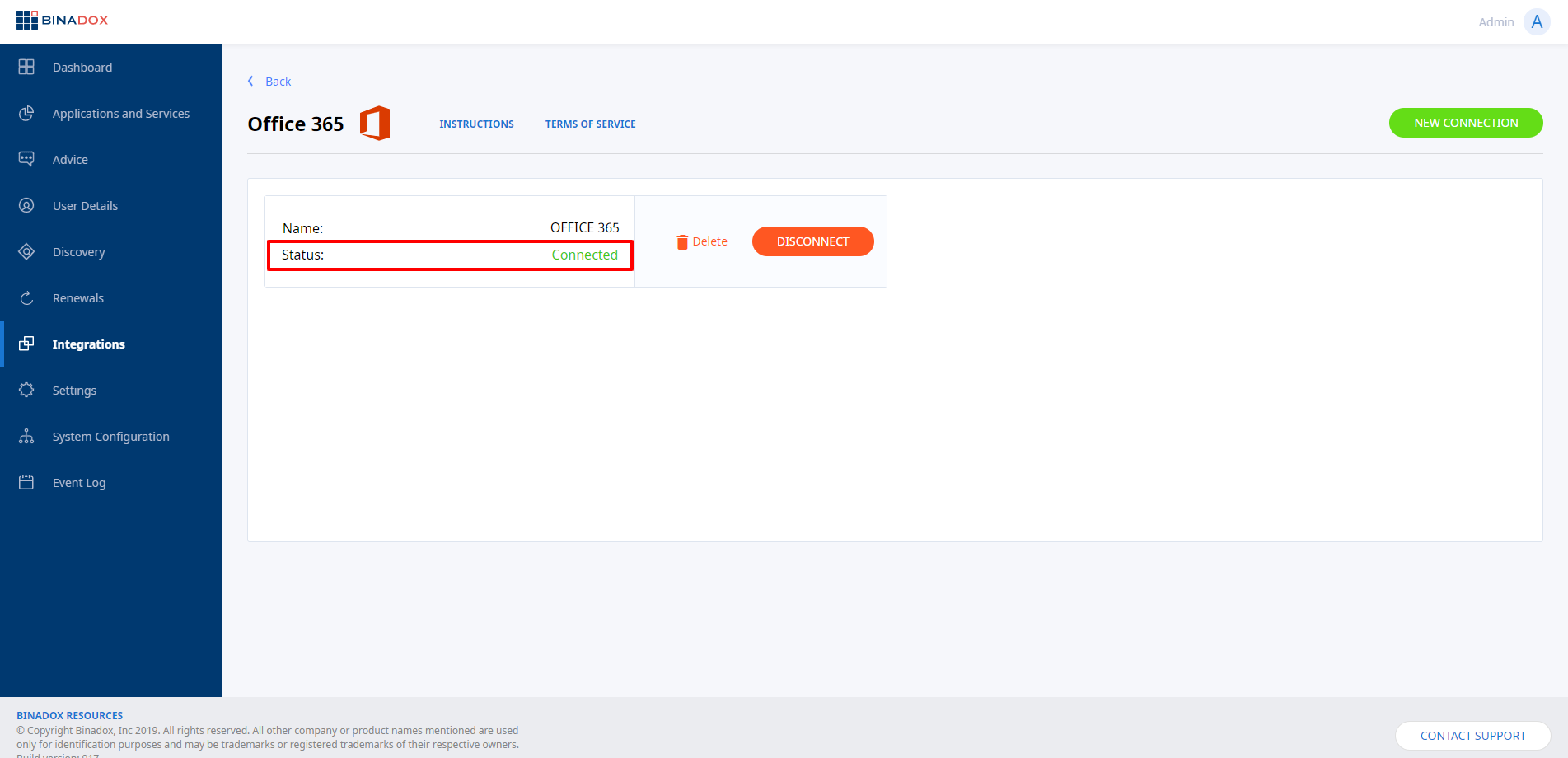
3. Create New Connection for Office 365 in Binadox
1. Log into your Binadox account.
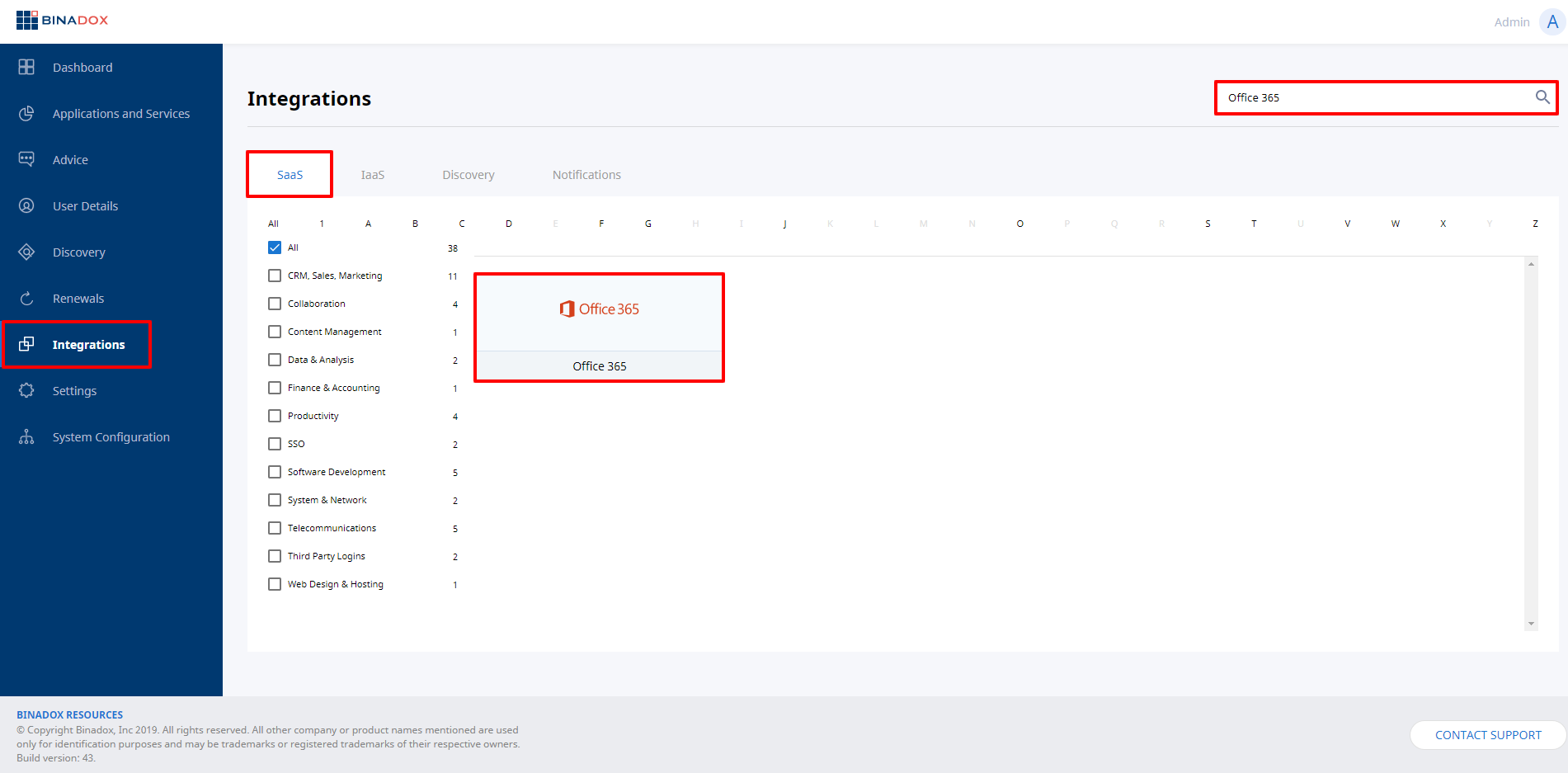
2. In the navigation pane on the left, click Integrations. Proceed to the SaaS tab. Click on the Office 365 icon. To quickly locate Office 365 in the list of available applications, type in its name in the search bar or use an alphabetical filter by clicking on the first letter of an application name, i.e. O.
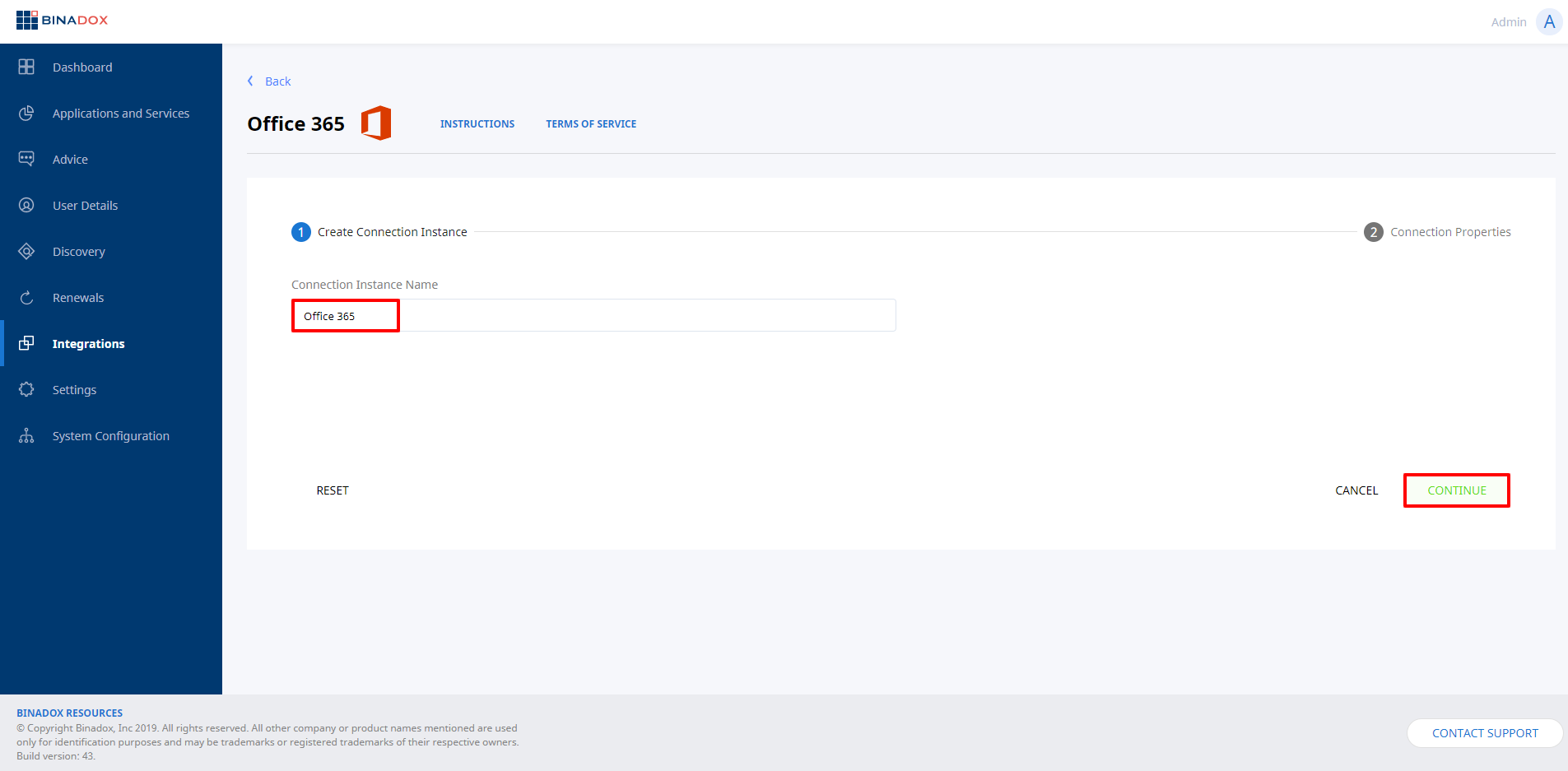
3. In the Office 365 view, type in the name of an instance in the Connection Instance Name field. Click Continue.
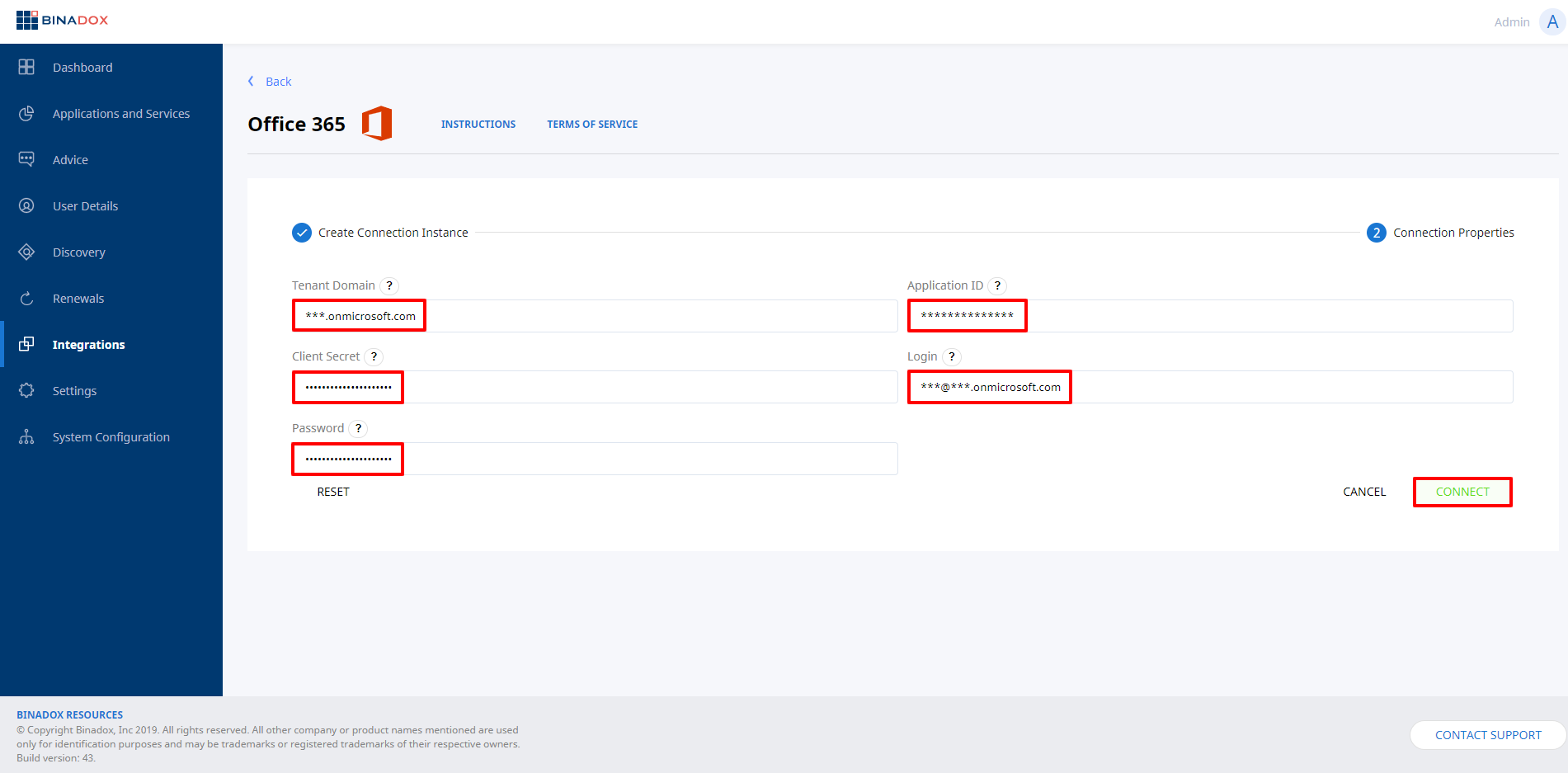
4. Fill in the required fields with parameters genereated automatically in PowerShell (see Clause 1 for step-by-step instructions) or manually on the Microsoft Azure portal and in the Microsoft 365 Admin Center (see Clause 2 for step-by-step instructions). Click Connect.
5. You will be redirected to the Microsoft login page.
IMPORTANT:
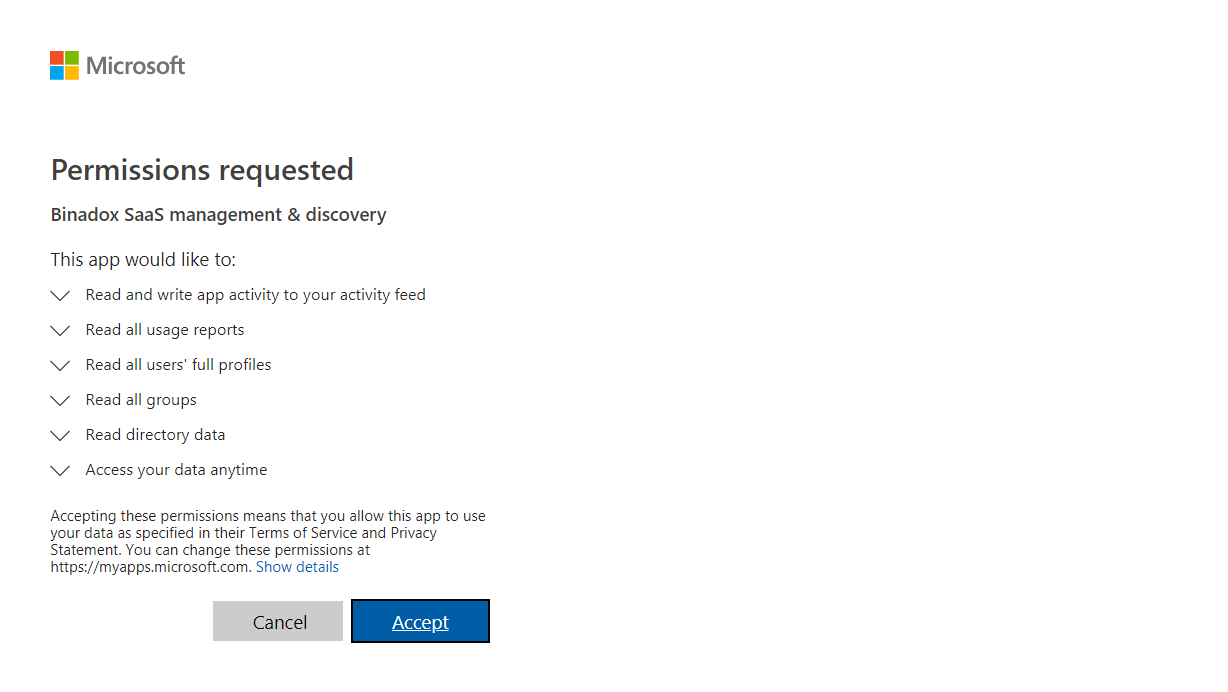
Admin permissions are required to grant Binadox access to read usage and cost data in the account. For this purpose, log in with administrator credentials.
6. In the appeared Permissions requested window, click Accept to give Binadox permissions to analyze data for spend and usage optimization.